Web3 Simplified - Why and How to Get your Web3
TL;DR
Everyone talks about Web3.
I was wondering if I could use some knowledge that I got while creating static sites with HUGO and its actually pretty simple.
Intro
Along the way, got to understand the difference between:
where something is and what something is thanks to the IPFS concept
The Web3 Revolution! > wait, what?
Today, we’re diving into the world of Web3, where decentralization, security, and innovation reign.
Ever wondered what all the buzz is about?
In this guide, we’ll demystify Web3 and show you just how easy it is to build your very own slice of the decentralized web.
We will do it in a simple three-step approach 📢
How can I optimize my browser for Web3 interaction?
- Ensure your browser supports Web3 protocols and technologies to seamlessly interact with decentralized applications and networks.
How do I create my website for Web3 compatibility?
- Build your website using web development tools and languages like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, ensuring compatibility with Web3 technologies.
How can I get my Web3 domain?
- Acquire a Web3 domain and securely link it to your decentralized website using technologies like the Ethereum Name Service (ENS) or InterPlanetary File System (IPFS).
Lets explore some potential of the next generation of the internet, the web3!
Exploring Web3 Concepts
Unstoppable Domains (UDs) 🚀
Unstoppable Domains are Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs), decentralized, and revolutionize the concept of domain ownership.
Unlike traditional domain names (e.g., .com), UDs are stored in the owner’s wallet like cryptocurrency, providing full control and autonomy.
Once acquired, there’s no need to worry about yearly renewal fees.
Plus, no third party can alter or seize them, ensuring digital ownership.
Get your NFT to your wallet: https://unstoppabledomains.com/search?searchTerm=noesloquetecrees
Remember to filter by the web3 ones!
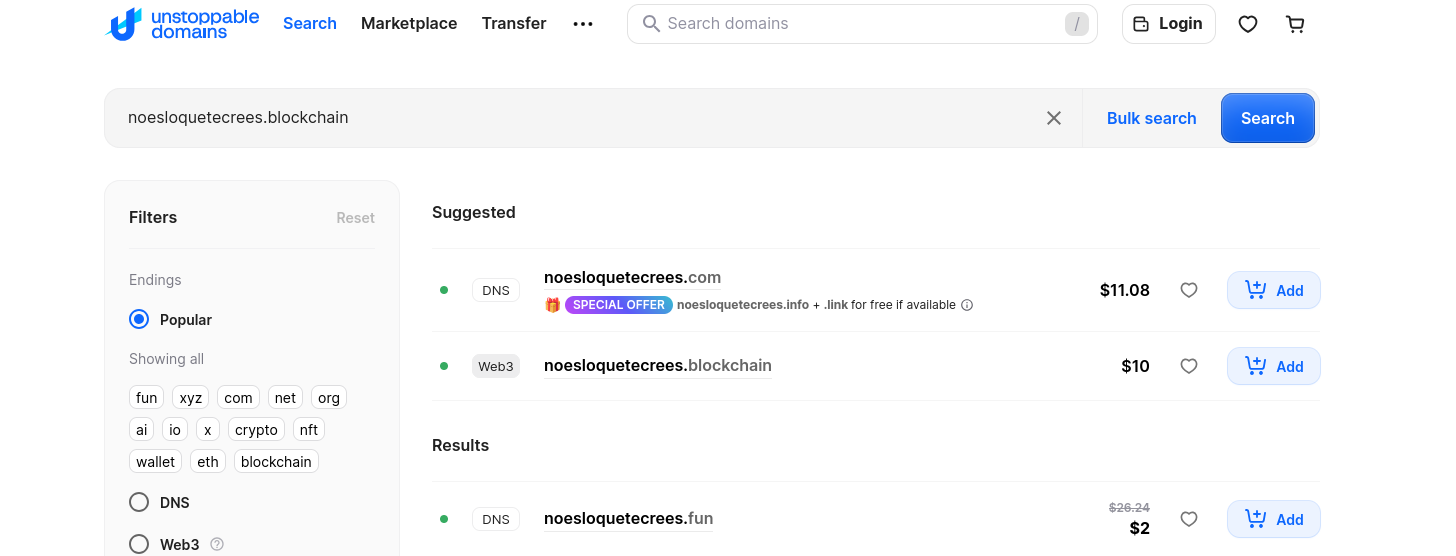
Unstoppable Web3 domains are minted (the process of turning your domain into a blockchain-based asset) across multiple blockchains including
IPFS: InterPlanetary File System 🛰️
IPFS, short for InterPlanetary File System, is a peer-to-peer hypermedia protocol with a visionary goal: to preserve and expand humanity’s knowledge.
By decentralizing content storage and distribution, IPFS aims to make the web more resilient, upgradable, and open.
It operates on a distributed network, where files are addressed by their content, not their location, facilitating faster and more efficient data retrieval.
Thanks to https://mariushosting.com/synology-install-ipfs-with-portainer/
More about IPFS below.
Points to Consider 🧐
Immutable Content 📜:
- New Versions, New CIDs: Uploading a new version of a file to IPFS results in a different cryptographic hash, assigning it a new CID (Content Identifier). This inherent feature ensures resistance to tampering and censorship. Changes to a file do not overwrite the original, and common chunks across files can be reused, minimizing storage costs.
Decentralized Truth 🌐:
- Absence of Central Authority: IPFS decentralization means there’s no single point of truth filtering out inaccurate or inappropriate content. While this empowers individuals and communities, it also underscores the importance of critical thinking. Remember, just because something is accessible doesn’t automatically make it true.
Embrace Critical Thinking 🤔:
- Wear Your Glasses of Critical Thinking: Whether the topic is the shape of the Earth or its position in the universe, approach information with skepticism. Always be prepared to question, verify, and analyze before accepting anything as truth.
In our digital age, where information is abundant and easily accessible, cultivating a mindset of critical thinking is essential. Let’s equip ourselves with these glasses every day to navigate the vast sea of information responsibly.
How to Start with Web3
- A Web3 compatible browser
- The Website files with your content
- A Web3 Domain
These allow dApps to run - For example you can try Brave Browser.
Why Brave?
Shortly because it supports Web3 out of the box and it is F/OSS:
Brave, a Chromium based F/OSS web browser that can be used for Web3
Making a Web3 without the sweat
The good news - Having your own Web3 is not that hard ✅
If you have already learned how to build a static website, you can automatically transfer that skill.
As the web moves towards a more decentralized and secure future with Web3 technologies, static Sites have an important role to play.
Since static sites are built with pure HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, they are compatible with Web3 technologies, such as blockchain-based domain names and decentralized storage solutions.
In fact, several projects have emerged that combine the benefits of static sites with the power of Web3.
For example, the Ethereum Name Service (ENS) allows users to register domain names that are stored on the Ethereum blockchain, making it possible to create decentralized and secure websites.
Similarly, the InterPlanetary File System (IPFS) is a decentralized storage system that can be used to host static sites, providing a more secure and resilient hosting solution.
Linking IPFS with a Web3 Domain
This part will cover how to host your files in IPFS and link them to your Web3 domain:
Option 1 - pinata.cloud:
- pinata.cloud: Currently offers a free tier after registration, allowing up to 100 files and 1GB storage.
Option 2 - Filebase:
- filebase: Allows you to try IPFS and Sia after registration.
- There is a free tier with no credit cards required.
- filebase: Allows you to try IPFS and Sia after registration.
The process is equivalent to set the DNS in a regular (web2.0) domain, but here, the domain and the IPFS are inmutable.
This is how it looks an Unestopable Domain at a wallet in polygonscan.
Thats right, it is the jalcocert.blockchain UD:
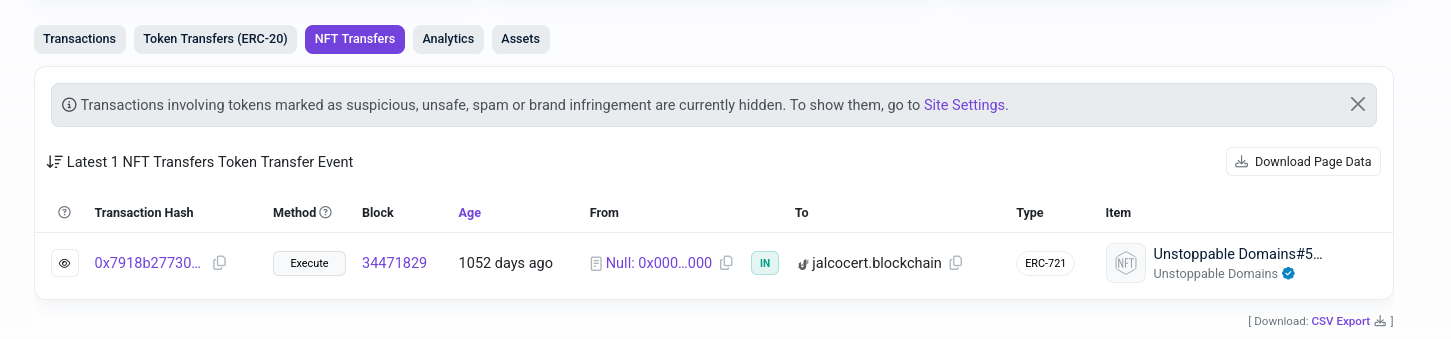
And I dont have to renew it ever again.
So if you navigate to via brave:
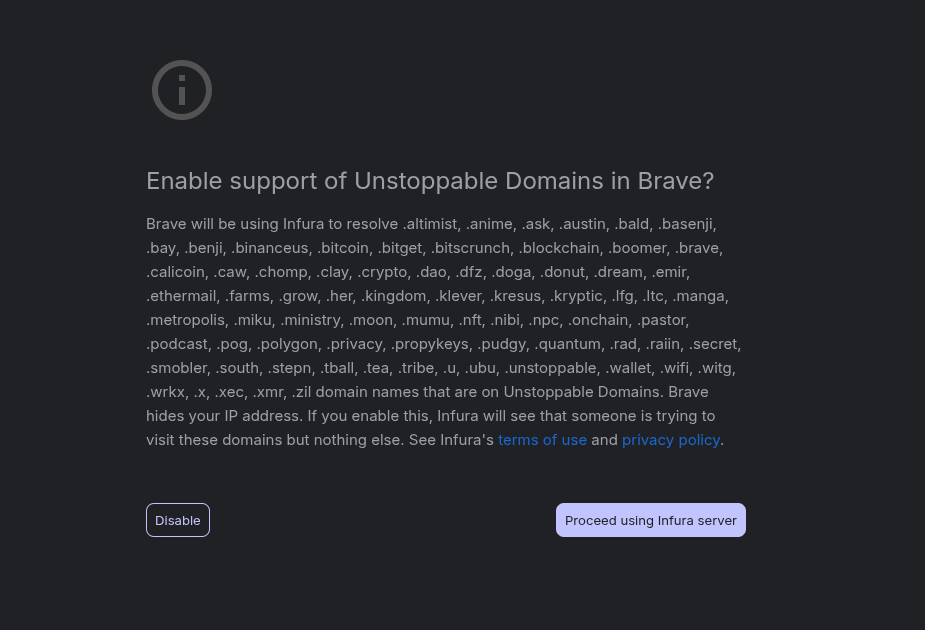
As of this moment, you will be directed to ipfs.io which I used to deploy: https://ipfs.io/ipfs/QmRxauMbq1pxp4wJrCovHaTpAQAXqneuYtrXj3feUu4KLp/
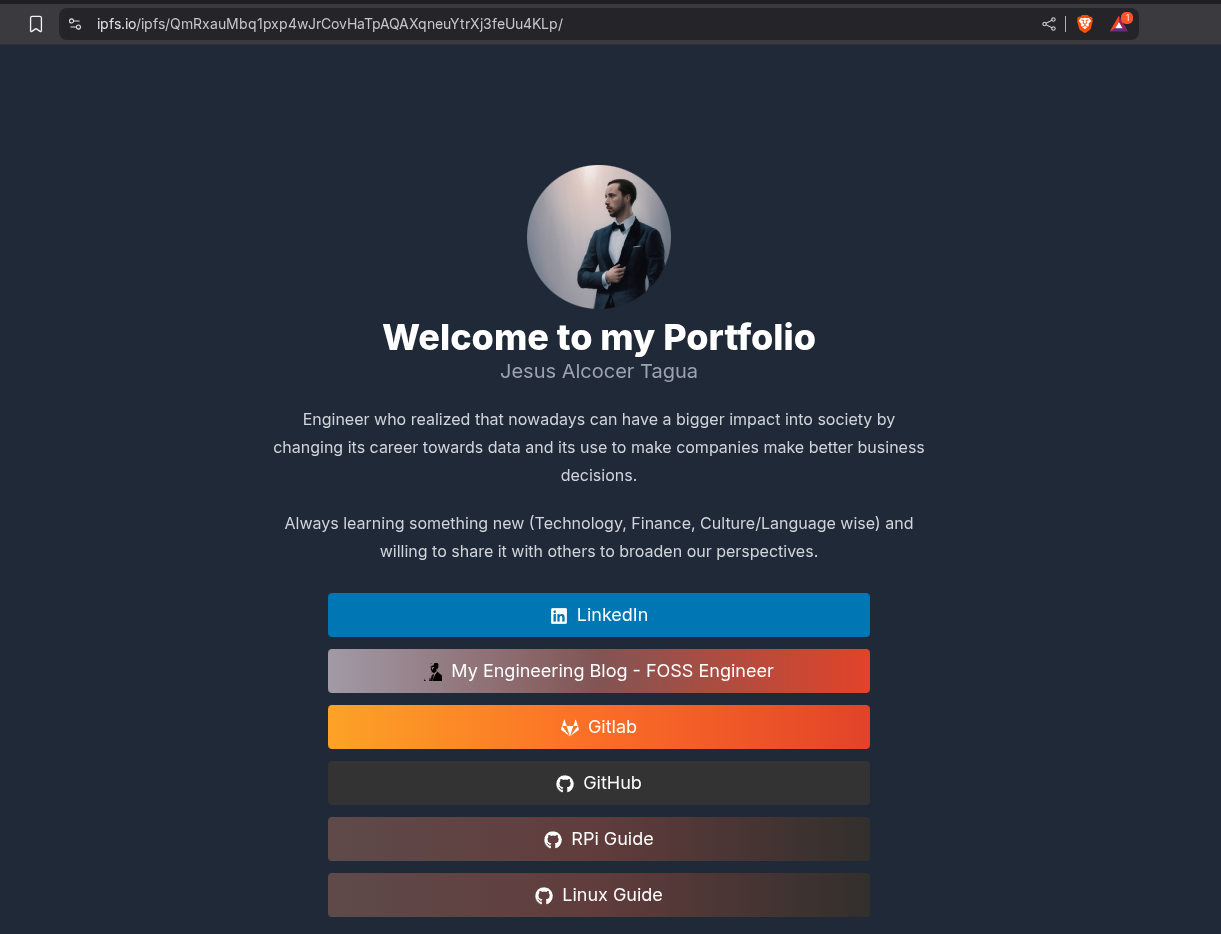
Which is nothing but my publicaly available HUGO Lynx theme as portfolio :)
Conclusion
I have this repository where I try to collect crypto / Web3 related stuff :)
Im also explorinw how to use Astro with GHPages in there.
- You might want to have a look to https://whycryptocurrencies.com/
FAQ
Learn more about Web3 at - https://learnweb3.io
How can I Build my compatible Web3
You can use a simple SSG, which will generate the html, css and js needed for the Web3 to be deployed and served.
Some Free tools to create a web3: HUGO, Astro, Jekyll…
ENS vs Unstoppable Domains
Ethereum Name Service (ENS) is like a decentralized, unstoppable version of the traditional Domain Name System (DNS), but it differs from Unstoppable Domains in a few key ways.
While both projects create domain names on a blockchain, they have different models for ownership and fee structures.
| Feature | Ethereum Name Service (ENS) | Unstoppable Domains |
|---|---|---|
| Blockchain | Ethereum | Multiple blockchains (e.g., Polygon, Ethereum) |
| Domain Ownership | Leased. You pay a yearly renewal fee to own the domain. If you don’t renew, it can expire and be purchased by someone else. | Owned outright. You pay a one-time fee and own the domain forever, like a non-fungible token (NFT). |
| Primary Use | Maps human-readable names (e.g., satoshi.eth) to long, alphanumeric crypto addresses. Also, it can link to decentralized websites. | Similar to ENS, it maps names (e.g., satoshi.crypto, satoshi.nft) to crypto addresses. Also, it focuses on providing a universal identity and login across Web3. |
| Goal | To build a decentralized naming system that is fully open and governed by the community through a DAO (Decentralized Autonomous Organization). | A private company that aims to simplify Web3 identities and domains with a one-time purchase model. |
The “Unstoppable” Aspect
The term “unstoppable” in both cases refers to the fact that these domains are stored on a blockchain.
This makes them:
- Censorship-Resistant: Once a domain is registered, no single company, government, or central authority can take it down or seize it.
- Tamper-Proof: The ownership record is stored on an immutable public ledger, making it nearly impossible to alter or counterfeit.
- Decentralized: Control and management are not in the hands of a single entity, unlike traditional DNS registrars like GoDaddy or Namecheap.
The main difference is that Unstoppable Domains emphasizes the lifetime ownership model, which is why it’s more synonymous with the term “unstoppable domain.”
However, ENS is also “unstoppable” in its own right, just with a different economic model based on renewals.
About IPFS
IPFS, or the InterPlanetary File System, is a peer-to-peer network protocol designed to store and share data in a distributed way.
Unlike the traditional web, which relies on a centralized location (a server) to host content, IPFS uses a content-addressing system.
Instead of asking “where” the content is located (like a URL), it asks “what” the content is, using a cryptographic hash to identify it uniquely.
This means multiple peers can host the same content, and a user can retrieve it from any peer that has it.
How IPFS Works
Traditional web protocols like HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) are location-based. When you type a URL, your browser sends a request to a specific server’s IP address to get the content. If that server is down or the content is moved, the link breaks.
IPFS, on the other hand, is content-addressed. When you add a file to the IPFS network, it’s broken into smaller chunks, and each chunk is given a unique cryptographic hash.
The main file is then represented by a single content identifier (CID), which is the hash of its root chunk.
To retrieve a file, you request the content by its CID, and the IPFS network finds the peers that have the data chunks.
You can then download the chunks from multiple peers simultaneously, which can be faster and more resilient.
Nothing new for P2P users :)
Key Features & Benefits ✨
- Decentralization: Data isn’t stored in a single location, making it resistant to censorship and single points of failure. If one server goes down, the content can still be accessed from other peers.
- Resilience & Durability: Because content is replicated across multiple nodes, it’s more durable and less likely to be lost. This is particularly useful for long-term data storage.
- Efficiency: By retrieving content from multiple nearby peers, IPFS can be faster and more bandwidth-efficient than traditional methods, especially for large files or in regions with limited connectivity.
- Censorship Resistance: Since the content isn’t tied to a specific server, it’s much harder for governments or other entities to block access to it.
IPFS vs Torrent
IPFS is similar to BitTorrent in that both are peer-to-peer (P2P) protocols that allow users to share files without relying on a centralized server.
However, they have fundamental differences in how they handle data and their overall purpose.
Key Similarities
- P2P Architecture: Both protocols operate on a decentralized network where users’ computers (nodes) connect directly to each other to share data.
- File Chunking: To make transfers more efficient, both IPFS and BitTorrent break files into smaller pieces (chunks). This allows a user to download different parts of a file from multiple peers simultaneously.
- Seeding/Pinning: In both systems, a file remains available as long as at least one user is hosting it. In BitTorrent, this is called “seeding,” while in IPFS, it’s called “pinning.”
How They Differ
| Feature | IPFS (InterPlanetary File System) | BitTorrent |
|---|---|---|
| Addressing | Content-based: Files are identified by a cryptographic hash (CID) of their content. The address is the content itself. | Location-based: A file is identified by a .torrent file or magnet link, which points to a specific “swarm” of peers. |
| Data Structure | A single, global, versioned file system. It’s designed to be a unified web where files can be linked and reused. | A protocol for individual one-off file transfers. Each torrent is its own separate “swarm.” |
| Deduplication | Automatically deduplicates content at the chunk level. If two files contain the same chunk, it’s only stored once on the network, saving space. | Does not have built-in deduplication. A user downloading a file with the same chunk from a different torrent will download it again. |
| Flexibility | Designed for a wider range of use cases, including hosting dynamic websites, applications, and streaming. | Primarily a file-sharing protocol for static files like movies or software. |
In short, while both are P2P protocols for file sharing, IPFS is a content-addressed system designed to be a global, decentralized web, while BitTorrent is a location-addressed system primarily for file distribution.