LLMs Function Calling
How to make so that LLMs will be using our already built tools?
Function Calling
Let’s imagine you have a super smart assistant (that’s your LLM) who can understand your requests in natural language.
However, sometimes you don’t just want an answer in words; you want the assistant to do something in the real world based on your request.
That’s where function calling comes in.
Think about Function calling like this 📌
You ask your assistant: “What’s the weather like in Warsaw?”
Without Function Calling:
The assistant might just give you a text answer: “The weather in Warsaw is currently sunny with a temperature of 15 degrees Celsius.” This is helpful information, but that’s all it can do.
With Function Calling:
You can tell the assistant that it has access to a special tool (a “function”) called get_weather(location).
- You ask: “What’s the weather like in Warsaw?”
- The LLM understands your intent: It recognizes that you’re asking about the weather and knows it has a function called
get_weatherthat can provide this information. - The LLM decides to use the function: Instead of just giving you a text answer, it decides to “call” the
get_weatherfunction. - The LLM provides the necessary information: To call the function, it needs to know the location. So, it extracts “Warsaw” from your question and provides it as the
locationargument to theget_weatherfunction. - The
get_weatherfunction does its job: This function (which is code you’ve written or that exists in a system) goes out, fetches the real-time weather data for Warsaw, and returns it in a structured format (like a piece of computer code). - The LLM receives the structured data: It gets back something like:
{ "temperature": 15, "conditions": "sunny", "humidity": 60 } - The LLM can now give you a more informative and dynamic answer: It can use this structured data to say something like: “The weather in Warsaw is currently sunny with a temperature of 15 degrees Celsius and a humidity of 60%.”
In essence, function calling allows the LLM to:
- Understand your intent to perform an action.
- Identify the right tool (function) to use.
- Extract the necessary information (arguments) from your request to use the tool.
- Use the tool and then potentially incorporate the results into its response.
Why is this useful?
- Real-world actions: LLMs can interact with external systems and perform actions like sending emails, booking flights, looking up information from databases, controlling smart devices, and much more.
- More accurate and up-to-date information: Instead of relying solely on its training data (which can be outdated), the LLM can fetch real-time information.
- Structured data: Functions often return data in a structured format, which is easier for other programs to understand and use.
- Extensibility: You can add new functions to give your LLM new capabilities
Key takeaways:
- Function calling lets LLMs go beyond just generating text and interact with the real world.
- It involves the LLM recognizing the need for an action and using a specific tool (function) to perform it.
- The LLM extracts the necessary details from your request to tell the function what to do.
Think of it as giving your super smart assistant hands and the ability to use tools to help you in more practical ways.
APIs + Function Calling 📌
Yes, absolutely! That’s a very accurate and important extension of the function calling concept.
In fact, calling APIs is one of the most common and powerful use cases for LLM function calling.
Here’s why:
APIs as the Gateway to External Data and Services: APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) are the standard way for different software systems to communicate with each other. They allow programs to request and exchange data or trigger actions on remote servers and services.
Functions as Wrappers for API Calls: When you define a “function” for the LLM to call, that function’s underlying code can very easily include making one or more API calls.
Let’s revisit the weather example with APIs in mind:
- You ask: “What’s the weather like in Warsaw?”
- The LLM decides to use the
get_weather(location)function. - The
get_weatherfunction’s code: Instead of directly knowing the weather, this function might contain code that makes an API call to a weather service (like OpenWeatherMap or a similar API). This API call would include thelocation(Warsaw) as a parameter. - The Weather API responds: The weather service’s API would send back structured data (usually in JSON format) containing the temperature, conditions, humidity, etc.
- The
get_weatherfunction processes the API response: It might extract the relevant information from the API response and return it in a consistent format back to the LLM. - The LLM uses this information to generate its final answer.
Other examples of function calling with API interactions:
- Booking a flight: The
book_flight(departure, destination, date)function could internally call an airline’s booking API. - Sending an email: The
send_email(recipient, subject, body)function could use an email service’s API (like SendGrid or Mailgun) to send the email. - Looking up product information: The
get_product_details(product_id)function could call an e-commerce platform’s API to retrieve product information. - Playing a song: The
play_song(artist, title)function could interact with a music streaming service’s API.
Function calling acts as the bridge that allows the LLM to leverage the vast capabilities exposed through APIs.
The functions you define serve as an abstraction layer, making it easier for the LLM to interact with complex external systems without needing to understand the intricate details of each API.
You define the function’s purpose and the LLM intelligently decides when and how to use it, including making the necessary API calls within that function’s implementation.
With OpenAI
Thanks to https://www.promptingguide.ai/applications/function_calling
How to use OpenAI API? Regular vs Function Calls
pip install openai==1.40.0api_key = os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY")
client = OpenAI(api_key=api_key)
#df = read_excel(file_name)
#df_markdown = df.to_markdown(index=False)
df_markdown="12345"
chat_completion = client.chat.completions.create(
messages=[
{
"role": "system",
"content": """
You are an expert data analyst.
""",
},
{"role": "user", "content": f"What it is this variable containing?: {df_markdown}"}
],
model="gpt-4o-mini",
temperature=0.3,
)
completed_message = chat_completion.choices[0].message.content
print(completed_message)And for function calling we would need to define which functions we have available and what they do:
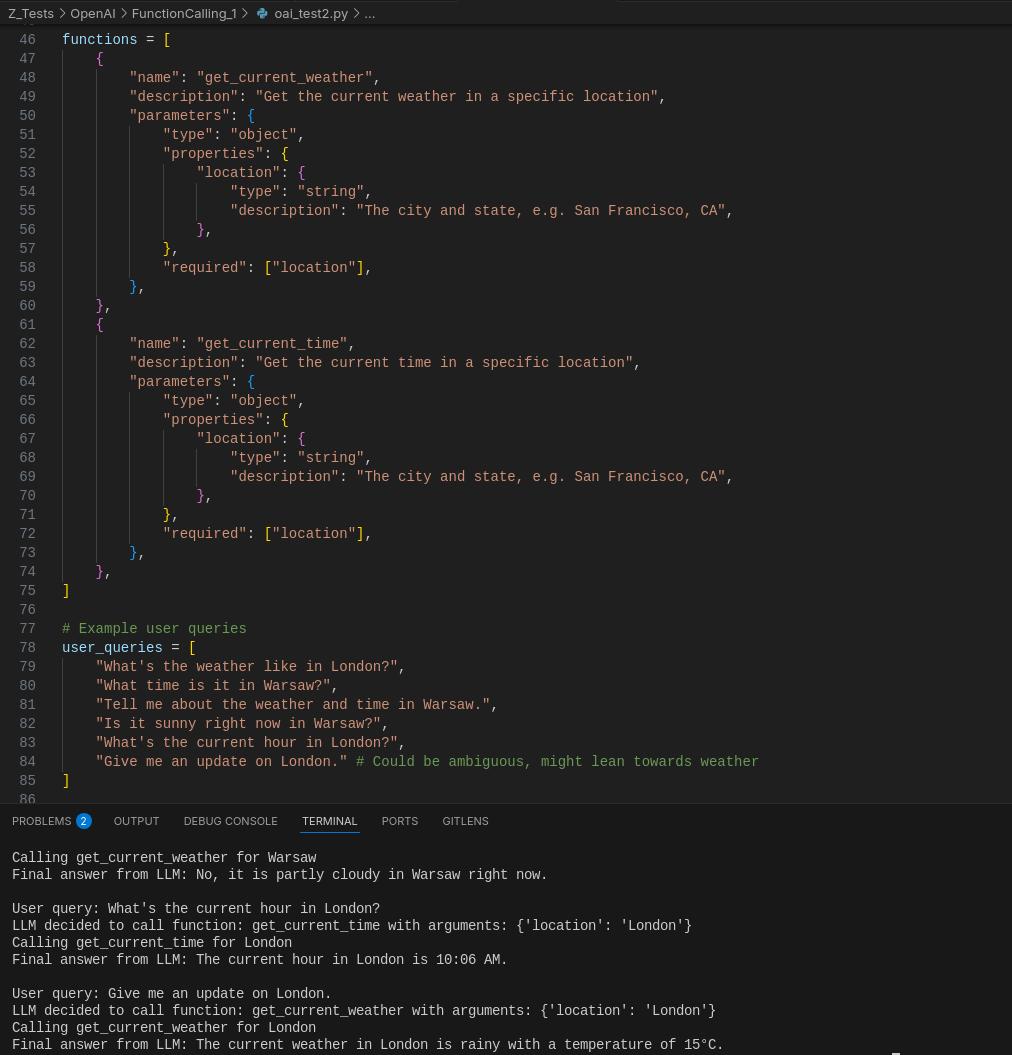
# 2. Define the function schema for OpenAI
functions = [
{
"name": "get_current_weather",
"description": "Get the current weather in a specific location",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The city and state, e.g. San Francisco, CA",
},
},
"required": ["location"],
},
}
]
# 3. User query
user_query = "What's the weather like in Warsaw right now?"
# 4. First API call to get the LLM's response and potential function call
response = openai.ChatCompletion.create(
model= "gpt-3.5-turbo", # Or another capable model
#"gpt-4o-mini",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": user_query}],
functions=functions, #THIS IS THE IMPORTANT DIFFERENCE THAT MAKE FUNCTION CALLING POSSIBLE!!!
function_call="auto", # Let the LLM decide when to call the function
)
response_message = response["choices"][0]["message"]Interesting Resources for Function Calling
ChatGPT returns natural text, and it can be unreliable. Returning functions makes the output more controlled and deterministic.
The feature can extract structured data from text (prompt) and assign them as arguments to a chosen function.
Developers can create their own functions connecting the LLMs to internal and external APIs and databases, and let the model decides which function to use and which arguments to pass.
Non-technical users can interact with LLMs to obtain data without having to know the underlying functions and required arguments.
Claude
How to use Anthropic API?
pip install anthropic==0.34.1 #https://github.com/anthropics/anthropic-sdk-pythonimport anthropic
client = Anthropic(api_key = os.getenv("ANTHROPIC_API_KEY"),)
system_prompt = "You are a helpful Data Analyst."
message = client.messages.create(
max_tokens=1024,
system=system_prompt, # Use the top-level "system" parameter
messages=[
{"role": "user", "content": "Hello, who you?"}
],
model="claude-3-5-sonnet-20240620",
#model="claude-3-opus-20240229",
)
#print(message.content)
content = message.content[0].text
print(content)Groq
Groq function calling via LiteLLM - https://docs.litellm.ai/docs/providers/groq#supported-models---all-groq-models-supported
Ollama
ollama run llama3.2See a sample here: https://github.com/JAlcocerT/Streamlit-MultiChat/tree/main/Z_Tests/OllamaAPI
Conclusions
There is another feature called Structured Outputs
..but we can see its all about the prompts!
Let’s break down the implementation details of function calling for OpenAI, Groq, and Claude, highlighting their differences.
1. OpenAI Function Calling
- Dedicated
functionsParameter: OpenAI provides a specificfunctionsparameter (now often referred to astoolswith atype: "function") in their Chat Completions API. This is a list of dictionaries, where each dictionary describes a function. - Schema Definition: Each function in the
functionslist requires aname, adescription, and aparametersobject. Theparametersobject follows a JSON Schema format, defining the expected properties (arguments), their types, and descriptions. Therequiredfield specifies mandatory parameters. - Model’s Decision: The OpenAI model analyzes the user’s query and the provided function descriptions and schemas. If it determines that a function call is appropriate, it responds with a
function_callobject in the API response. This object contains thenameof the function to be called and thearguments(as a JSON string) that the model believes should be passed to that function. - Execution by the Developer: It’s the developer’s responsibility to:
- Parse the
function_callobject. - Execute the actual function with the provided arguments in their own codebase.
- Make another API call to OpenAI, including the original user query, the model’s function call response, and a
function_responsemessage containing the result of the function execution. This allows the model to incorporate the function’s output into its final natural language response to the user.
- Parse the
- Control over Function Calling: The
function_callparameter in the initial API request can be set to"auto"(let the model decide),"none"(force text response), or to a specific function name to force that function to be called. - Structured Outputs (June 2024): OpenAI introduced “Structured Outputs” with the
strict: truesetting in the function definition, guaranteeing that the arguments generated by the model precisely match the provided JSON schema.
Example (Conceptual OpenAI):
response = openai.ChatCompletion.create(
model="gpt-3.5-turbo",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": "What's the weather in Warsaw?"}],
functions=[
{
"name": "get_current_weather",
"description": "Gets the current weather in a given location",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {"location": {"type": "string"}},
"required": ["location"],
},
}
],
function_call="auto",
)
if response["choices"][0]["message"].get("function_call"):
function_name = response["choices"][0]["message"]["function_call"]["name"]
arguments = json.loads(response["choices"][0]["message"]["function_call"]["arguments"])
weather_result = get_current_weather(location=arguments["location"])
# ... subsequent API call with function response ...2. Groq Function Calling (Tool Use)
- Tool Use via Prompting and Structured Output: Groq’s approach to function calling, which they refer to as “Tool Use,” relies on instructing the model through the prompt to output a structured JSON object that represents a function call.
toolsParameter in Chat Completions: The Groq API’schat.completions.createendpoint supports atoolsparameter, which is an array describing the available functions (tools). The structure is similar to OpenAI’sfunctions, includingname,description, andparametersdefined using JSON Schema.tool_choiceParameter: Groq provides atool_choiceparameter, similar to OpenAI’sfunction_call, allowing you to set it to"none","auto", or force a specific tool to be used with{"name": "tool_name"}.- Model’s Output: When the Groq model decides to use a tool, its response will include a
tool_callsobject, which contains details about the function to be called (includingid,name, andparameters). - Developer Execution and Subsequent Call: The developer follows a similar pattern to OpenAI: parse
tool_calls, execute the function, and then make another API call to Groq, including the tool’s output in themessagesarray to inform the model’s final response. - Compatibility with OpenAI Tool Calls: Groq has designed its tool call structure to be largely compatible with OpenAI’s, making it potentially easier to adapt applications built for OpenAI.
Example (Conceptual Groq):
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="mixtral-8x7b-32768",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": "What's the weather in Warsaw?"}],
tools=[
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_current_weather",
"description": "Gets the current weather in a given location",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {"location": {"type": "string"}},
"required": ["location"],
},
},
}
],
tool_choice="auto",
)
if response.choices[0].message.tool_calls:
tool_call = response.choices[0].message.tool_calls[0].function
function_name = tool_call.name
arguments = json.loads(tool_call.arguments)
weather_result = get_current_weather(location=arguments["location"])
# ... subsequent API call with tool_outputs ...3. Claude Function Calling (Tool Use)
- Tool Use via Messages API: Claude’s function calling (also referred to as “Tool Use”) is implemented through the Messages API (
/v1/messages). You define the available tools within thetoolsparameter of themessages.createrequest. - Tool Definition: The
toolsparameter is a list of tool dictionaries. Each tool has aname, adescription, and aninput_schemathat follows JSON Schema to define the expected parameters. - Model’s Request for Tool Use: When Claude determines that a tool should be used, the API response will have a
stop_reasonof"tool_use". Thecontentof the assistant’s message will be empty, and thetool_callsarray will contain details about the tool to be called, including thenameand thearguments(as a JSON object). - Developer Execution and Subsequent Call: Similar to OpenAI and Groq, the developer executes the identified tool with the provided arguments. The result is then sent back to Claude in a subsequent
messages.createrequest as a new message with theroleset to"tool_result", including thetool_call_idand thecontentof the result. - Multi-Step Process: The interaction with Claude for tool use typically involves multiple turns of the conversation within the
messagesarray.
Example (Conceptual Claude):
response = client.messages.create(
model="claude-3-opus-20240229",
max_tokens=300,
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": "What's the weather like in London?"}],
tools=[ #THIS IS THE COOL STUFF
{
"name": "get_current_weather",
"description": "Gets the current weather in a given location",
"input_schema": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {"location": {"type": "string"}},
"required": ["location"],
},
}
]
)
if response.stop_reason == "tool_use":
tool_call = response.tool_calls[0]
function_name = tool_call.name
arguments = tool_call.arguments
weather_result = get_current_weather(location=arguments["location"])
# ... subsequent API call with tool_results in the messages array ...Key Differences Summarized:
| Feature | OpenAI | Groq | Claude |
|---|---|---|---|
| API Parameter | functions (in ChatCompletion.create) | tools (in chat.completions.create) | tools (in messages.create) |
| Tool Definition | name, description, parameters (JSON Schema) | type: "function", function: {name, description, parameters} (JSON Schema) | name, description, input_schema (JSON Schema) |
| Model’s Call | function_call object in response | tool_calls object in response | stop_reason: "tool_use", tool_calls array |
| Control | function_call parameter (auto, none, specific function) | tool_choice parameter (none, auto, specific tool) | Implicit in prompt and tool definition |
| Subsequent Call | function_response message | tool_outputs in messages array | tool_results message in messages array |
| API Endpoint | ChatCompletion.create | chat.completions.create | messages.create |
While the underlying concept of describing functions and having the LLM decide when and how to use them is similar across these APIs, the specific parameter names, the structure of the tool/function definitions, and the format of the model’s response indicating a tool call differ.
Example of system Prompt that works well for me
#python3 pyopen.py > output.mdx
import os
from dotenv import load_dotenv
from openai import OpenAI # pip install openai==1.30.5
# Load environment variables from the .env file
load_dotenv()
# Get the OpenAI API key from the environment variables
api_key = os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY")
# Initialize the OpenAI client
client = OpenAI(
api_key=api_key,
)
mtg_must_have= """
* Purpose - Every meeting should have an objective—the reason why you're having the meeting. Before you schedule a meeting be sure you know what it is that you want out of the meeting.
* Agenda - An agenda outlines the plan for the meeting and lets participants know what to expect. It allows them to be prepared so they can actively participate and bring their expertise to the table.
* preparation - Before the meeting all participants should take some time to review the agenda and prepare any questions they may have.
"""
system_reminder = """
Never start your answers with "As an AI language model" when responding to questions.
No disclaimer is needed in any situation.
Write using simple language so a grandma could understand.
Use a conversational tone, be informal and approachable. Write like how people in real life would talk. A bit of slang is okay but don't overdo it.
If you don’t know the answer, just say you don’t know.
Your answers should be on point, succinct and useful. Each response should be written with maximum usefulness in mind rather than being polite.
If something seems out of reach, don’t ask the user to do it; instead, try to work through all your available options first.
When solving problems, take a breath and tackle them step by step.
My career depends on you giving me a good answer
Speak only what needs to be said. Keep the responses brief and to the point, avoid extra words and overly long explanations.
"""
chat_completion = client.chat.completions.create(
messages=[
{
"role": "system",
"content": f"""You are an expert meeting assistant. Very aware of the following:
{mtg_must_have}
Remember also, that: {system_reminder}
""",
},
{"role": "user", "content": "Who are you and what can you do?"}
],
model="gpt-4o-mini",
temperature=0.7,
)
# Extract and print the content of the completed message
completed_message = chat_completion.choices[0].message.content
print(completed_message)FAQ
About LangChain and Frameworks
Interesting Article - https://www.octomind.dev/blog/why-we-no-longer-use-langchain-for-building-our-ai-agents
However, as their requirements became more sophisticated, LangChain’s rigid high-level abstractions turned into a source of friction and hindered productivity.
Issues with LangChain’s abstractions were…
- The Main Issues with LangChain’s Abstractions
- 🚧 Increased complexity of code without perceivable benefits
- 🤔 Difficulty in understanding and maintaining code
- 🔒 Inflexibility in adapting to new requirements
- 🕸️ Nested abstractions leading to debugging internal framework code
Octomind’s development team faced challenges when trying to implement more complex architectures, such as spawning sub-agents or having multiple specialist agents interact with each other. LangChain’s limitations forced them to reduce the scope of their implementations.
- Building AI Applications Without a Framework
After removing LangChain, Octomind realized that a framework might not be necessary for building AI applications. Instead, they suggest using a building blocks approach with simple low-level code and carefully selected external packages. The core components most applications need are:
- 💬 A client for LLM communication
- 🛠️ Functions/Tools for function calling
- 📊 A vector database for RAG
- 🔍 An Observability platform for tracing, evaluation, etc.
By using modular building blocks with minimal abstractions, Octomind’s team can now develop more quickly and with less friction, focusing on solving problems rather than translating ideas into framework-specific code.
Dont marry the framework? :)
Generating Images with OpenAI
You can use Dalle Text2Image models via the openAI API
Understanding Images with Claude
ReAct (vs) Function Calling
🛠️ Function Calling Agents
Function calling agents rely on the vendor to select the correct tools and inputs based on a provided schema, shifting the responsibility of tool selection to the vendor.
This approach is similar to the serverless model and is supported by many vendors, with LangChain providing an abstraction for easy switching between models.
🔧 Vendor-driven tool selection 🌐 Serverless-like model 🔄 Easy switching between models with LangChain abstraction 🧠 ReACt Agents
Now let’s see ReACt agents use the ReACt prompter, which is based on the ReACt paper and incorporates prompt engineering techniques.
This approach makes the LLM a reasoning engine, selecting tools and inputs itself. ReACt agents offer more control and flexibility to developers but require more work and thinking in the tool selection process.
Key points:
🎨 Developer-driven tool selection 📜 Based on the ReACt paper 🔧 Incorporates prompt engineering techniques 🔍 LLM acts as a reasoning engine 🛠️ More control and flexibility for developers 🤔 Requires more work and thinking from developers 🤔 Choosing the Right Approach
The choice between function calling agents and ReACt agents depends on the level of control and flexibility desired by the developer.
Function calling agents provide ease of use but less control, while ReACt agents offer more control but require more effort from the developer.
LangChain - AgentsExecutors
AI Agents
What could ReAct enhance? Two projects in mind 🚀
- Streamlit Multichat and the YT Summarizer with Groq from PhiData
version: '3'
services:
streamlit_multichat:
image: ghcr.io/jalcocert/streamlit-multichat:latest
container_name: streamlit_multichat
volumes:
- ai_streamlit_multichat:/app
working_dir: /app
command: /bin/sh -c "\
mkdir -p /app/.streamlit && \
echo 'OPENAI_API_KEY = \"sk-proj-oaiapi\"' > /app/.streamlit/secrets.toml && \
echo 'GROQ_API_KEY = \"gsk_yourgroqapi\"' >> /app/.streamlit/secrets.toml && \
echo 'ANTHROPIC_API_KEY = \"sk-ant-anthapikey-\"' >> /app/.streamlit/secrets.toml && \
streamlit run Z_multichat_Auth.py"
ports:
- "8501:8501"
networks:
- cloudflare_tunnel
restart: always
# - nginx_default
networks:
cloudflare_tunnel:
external: true
# nginx_default:
# external: true
volumes:
ai_streamlit_multichat:version: '3.8'
services:
phidata_service:
image: ghcr.io/jalcocert/phidata:yt-groq #phidata:yt_summary_groq
container_name: phidata_yt_groq
ports:
- "8502:8501"
environment:
- GROQ_API_KEY=gsk_yourgroq_apikey # your_api_key_here
command: streamlit run cookbook/llms/groq/video_summary/app.py
restart: always
# networks:
# - cloudflare_tunnel
# networks:
# cloudflare_tunnel:
# external: true