Jira 101 vs ADO | PDF to md with Kreuzberg
TL;DR
As tech lead, you will need to analyze requirements/proposal to clients.
+++ Create the technical solution document in pdf and probably create some ppt with slidev.
Intro
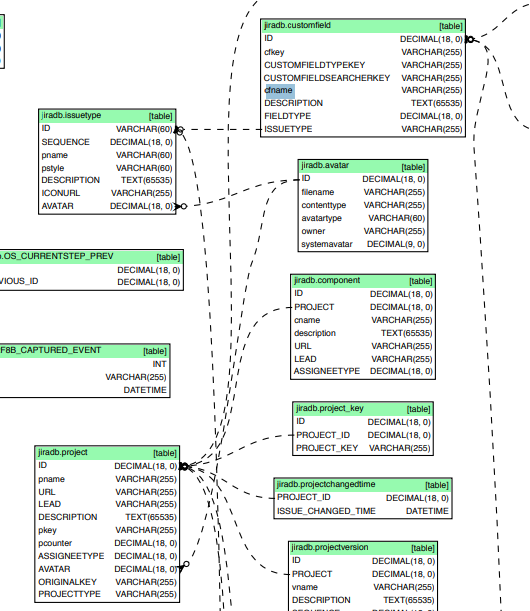
To work with Jira, you need to understand their datamodel: https://developer.atlassian.com/server/jira/platform/database-schema/
Also with Jira API docs: https://developer.atlassian.com/cloud/jira/platform/rest/v3/intro/#about
And some apps in atlassian marketplace like https://marketplace.atlassian.com/apps/1221150/power-bi-connector-for-jira?tab=overview
Just in case you need to build a PBi x Jira related dashboard.
Instead of a https://eazybi.com/products/eazybi-reports-and-charts-for-jira
On the jira data model pdf, you will find jiradb.table_name, like jiradb.issuetype
I got a interesting task and could not avoid to think about how to do it with:
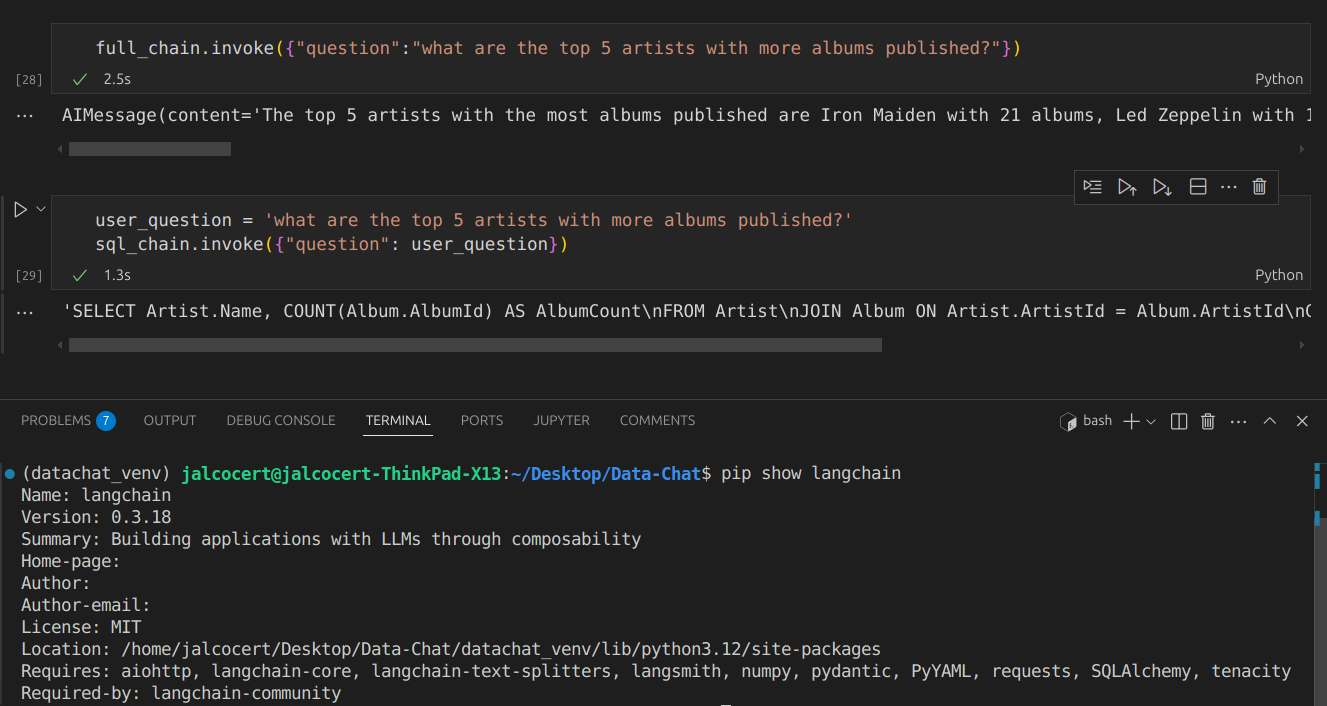 LangChain chat with DB | Post
LangChain chat with DB | PostSo how about taking the requirements from PdM, understand Jira schema and propose some architectural solution?
What I learnt
For me, Pandoc is a tool that is here to stay.
- Convert that
.mdinto a pdf:
git clone https://github.com/JAlcocerT/jira-datamodel
cd jira-datamodel
#thank you, next
sed 's/✅/[OK]/g; s/❌/[X]/g; s/��/[CHART]/g' reply-overview-final.md > input-clean.md
pandoc input-clean.md -o requirements-jiraado-estimation8.pdf --pdf-engine=xelatex --toc- If you are not conviced yet, use Pandoc to create a
pdf from mdand have a cool theme
Like https://github.com/enhuiz/eisvogel
A pandoc LaTeX template to convert markdown files to PDF or LaTeX.
- You can potentially use Pandoc with CSS to generate your pdfs:
sudo apt-get install wkhtmltopdf
pandoc 1-3-summary-embedded.md -o styled-summary.pdf --pdf-engine=wkhtmltopdfAnd this can (and will) not only simplify your reports.
But it can be use for that cool LandThatJob.
because you havent forgot on the Overleaf CV generation, right?
CV as a code, like with overleaf + your story + AI magic with a given offer link, aka scrap & process = you getting the job you want
Conclusions
Whatever you have analyzed and created a md->pdf report with it…
You can make a quick PPT by tweaking the .md to the slidev way (with corporate background as well).
Just see this one from slidev-editor.
#npm i -D playwright-chromium
npx slidev export --format pptx #ppt from md thanks to SliDevJS
npm init slidev #yarn create slidev
npm run dev
#npm run dev -- --host 0.0.0.0 --port 4321 #http://192.168.1.11:4321/
#rm -rf .git
npm run build
#cd ./dist
#npx serve
#npx playwright install
#npx slidev export --format pptx --output my-presentation.pptx
#npx slidev export --format pptx --range 1-5,8,10-12Or to pdf: which might not work
#npx playwright install
npx slidev export --format pdf
npx slidev export --format pdf --range 1-5,8,10-12Remember about
http://localhost:3030/overview/or/exporterwhere you will get the
The discussion about REST APIs is a critical part of how these systems handle data and integrate with the outside world.
| Feature | Jira REST API | Azure DevOps (ADO) REST API |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Query Language | $\text{Jira Query Language (JQL)}$ | $\text{Work Item Query Language (Wiql)}$ |
| Query Strength | Extremely powerful for searching/filtering work items (Issues) based on fields, links, projects, and version data. | Excellent for structured hierarchy queries (parent/child, tree-based links) and complex team-based filters. |
| API Architecture | Issue-centric. The core API revolves around Issues and their fields. Other APIs are specific (e.g., Agile, GreenHopper, Software, Service Management). | Service-centric (Modular). Divided into separate, distinct REST APIs for each service: $\text{Boards}$, $\text{Repos}$, $\text{Pipelines}$, $\text{Test}$, $\text{Artifacts}$. |
| Custom Fields Access | Highly flexible. Custom fields are easily accessible and modifiable using standard field ID notation in the Issue API (e.g., customfield_10001). | Highly structured. Custom fields are accessed via a field reference name (e.g., Custom.TargetReleaseName) within the Work Item API. |
| Updating Work Items | Uses standard JSON payloads to update fields. Complex custom logic often requires Jira Automation or a Marketplace app/hook. | Uses the JSON Patch standard for updates, which defines specific operations ($\text{add}$, $\text{replace}$, $\text{remove}$) for precise changes. |
| Extensibility Focus | API is used primarily for Data Exchange and integrating with third-party, specialized tools (CI/CD, CRM, etc.). | API is used for Full Automation of the DevOps lifecycle (creating builds, deploying releases, managing repos, as well as managing work). |
| \ |
- Jira favors a query-first, data-flexible approach. JQL is an incredibly human-readable and powerful language for pulling specific work items. The core API is focused on the issue as the unit of work.
- Azure DevOps favors a structured, command-and-control approach. Wiql is very strong for hierarchical queries, and the API is organized across the entire toolchain, allowing for deep automation of every part of the DevOps process (build, release, testing, and work).
FAQ
The main difference between Pandoc and LaTeX is their purpose and function:
- LaTeX is a high-quality typesetting system primarily used for creating well-formatted documents, especially those with complex mathematical formulas, scientific papers, and academic publications.
It involves writing documents in a markup language focused on presentation, layout, and formatting control. LaTeX is a document preparation system rather than a conversion tool.
- Pandoc is a universal document converter. It converts text documents between many markup formats like: Markdown, LaTeX, HTML, Word, and PDF. Pandoc is often used to write content in a simpler markup (e.g., Markdown) and then convert it into well-structured formats including LaTeX for further processing or PDF generation.
Pandoc can also convert LaTeX to other formats.
In summary:
- LaTeX is a typesetting system and markup language for creating documents with precise formatting.
- Pandoc is a tool that converts documents from one markup format to another, including to and from LaTeX, enabling flexible workflows.
Thus, LaTeX is used for authoring and typesetting documents directly, while Pandoc acts as a bridge or converter supporting multiple document formats, including LaTeX, as one of its output options.
Jira API with JiraTUI
MIT | A Textual User Interface for interacting with Atlassian Jira from your shell
PDF to md/json
To just read PDFs you can try Okular: but the ctrl+F worked better for me with Zen or firefox
#sudo apt install okularSeveral open source tools can help convert complex PDFs, such as database schemas from jira, into machine-readable formats like JSON, XML, or structured diagrams.
Some notable open source options are:
MIT | A PDF to Markdown converter
- Tabula: A popular tool for extracting tables from PDFs into CSV, JSON, or Excel formats. It’s especially useful for schema diagrams presented as tables.
PDF-Extract-Kit: A toolkit that uses layout and text analysis to extract structured data, including tables, from PDFs. It supports conversion to JSON, which can be processed further.[2]
PyMuPDF (fitz): A Python library to extract text, images, and layout information from PDFs, which can be combined with other tools to create structured data.
Camelot: Similar to Tabula, designed to extract tables from PDFs into pandas DataFrames, then exported as JSON or CSV.
OpenDataLab https://github.com/opendatalab/PDF-Extract-Kit
Apache v2 | Convert documents to structured data effortlessly. Unstructured is open-source ETL solution for transforming complex documents into clean, structured formats for language models.
Transforms complex documents like PDFs into LLM-ready markdown/JSON for your Agentic workflows.
Apache v2 \ Toolkit for linearizing PDFs for LLM datasets/training
MIT | Easily deployable and scalable backend server that efficiently converts various document formats (pdf, docx, pptx, html, images, etc) into Markdown. With support for both CPU and GPU processing, it is Ideal for large-scale workflows, it offers text/table extraction, OCR, and batch processing with sync/async endpoints.
A modern, user-friendly web application that converts PDF documents to clean, formatted Markdown text.
Convert PDF to HTML without losing text or format.
Convert documents to structured data effortlessly. Unstructured is open-source ETL solution for transforming complex documents into clean, structured formats for language models.
OCRFlux is a lightweight yet powerful multimodal toolkit that significantly advances PDF-to-Markdown conversion, excelling in complex layout handling, complicated table parsing and cross-page content merging.
MIT | Using GPT to parse PDF
MIT | Plumb a PDF for detailed information about each char, rectangle, line, et cetera — and easily extract text and tables.
Plumb a PDF for detailed information about each text character, rectangle, and line. Plus: Table extraction and visual debugging.
- https://github.com/pymupdf/PyMuPDF ✅ local working and no keys + good docs
#cd z-PyMuPDF
#pip install PyMuPDF
uv init
uv add PyMuPDF
uv run ./z-PyMuPDF/test-pymupdf.pyPyMuPDF is a high performance Python library for data extraction, analysis, conversion & manipulation of PDF (and other) documents.
Apgl v3 | Transforms complex documents like PDFs into LLM-ready markdown/JSON for your Agentic workflows.
MIT | A maroto way to create PDFs. Maroto is inspired in Bootstrap and uses gofpdf. Fast and simple.
- https://github.com/QuivrHQ/MegaParse ❌ error with sample script from readme
File Parser optimised for LLM Ingestion with no loss 🧠 Parse PDFs, Docx, PPTx in a format that is ideal for LLMs.
- https://github.com/datalab-to/marker ✅❌ local and working, but too slow (30s for a cv!)
gpl 3 | Convert PDF to markdown + JSON quickly with high accuracy
git clone https://github.com/JAlcocerT/jira-datamodel
#cd z-test-quivir-megaparse
#cd - https://github.com/wisupai/e2m ❌ too long to download dependencies
Apache v2 | E2M converts various file types (doc, docx, epub, html, htm, url, pdf, ppt, pptx, mp3, m4a) into Markdown. It’s easy to install, with dedicated parsers and converters, supporting custom configs. E2M offers an all-in-one, flexible, and open-source solution.
Apache v2 | A powerful tool that leverages multimodal large language models to transcribe PDF files into Markdown format.
- https://github.com/Goldziher/kreuzberg ✅ Works locally via container exposing an API, very fast and no LLM Keys ✅✅
#cd z-kreuzberg
# Extract text from any file to text format
#uvx kreuzberg extract document.pdf > output.txt
uvx 'kreuzberg[cli]' extract jira-estimation.pdf > output.txt
uvx 'kreuzberg[cli]' extract jira-7-9-2-database-schema.pdf > output2.txt
###with container even better!
docker run -p 8027:8000 goldziher/kreuzberg
curl -X POST -F "file=@sample-cv.pdf" http://localhost:8027/extract
curl -X POST -F "file=@jira-estimation.pdf" http://localhost:8027/extract
curl -X POST -F "file=@jira-7-9-2-database-schema.pdf" http://localhost:8027/extractMIT | Document intelligence framework for Python - Extract text, metadata, and structured data from PDFs, images, Office documents, and more. Built on Pandoc, PDFium, and Tesseract.
When deployed into your homelab, simply:
curl -X POST -F "file=@20251026-1956-0737-wniosek.pdf" http://192.168.1.2:8027/extract
curl -X POST -F "file=@20251026-1956-0737-wniosek.pdf" http://192.168.1.2:8027/extract > sample-pdf-to-text.txt
#http://jalcocert-x300-1:8027/
#time curl -X POST -F "file=@BTC-standard.pdf" http://192.168.1.2:8027/extract > sample-pdf-to-text2.txt #1second ✅
#wc -m sample-pdf-to-text2.txt 600kMD to epub
Just in case you want to put together a epub ebook from markdown (with a cool cover): https://github.com/JAlcocerT/sell-your-ebook/tree/main?tab=readme-ov-file#-creating-epub-from-cover-image
convert "1-dna-analytics/Ebook-cover-SSGs.png" -resize 1200x1800\> "cover.jpg" && \
echo -e "# Cover\n" > content.md && \
pandoc -o "Ebook-cover-SSGs.epub" --epub-cover-image="cover.jpg" --metadata title="Ebook Cover" content.md
#&& \
#rm -f cover.jpg content.mdThe cover is not full page, but you get the idea.
And epub to pdf
pandoc "Ebook-cover-SSGs.epub" -o "renderedPDF.pdf"
#pandoc "Ebook-cover-SSGs.epub" -o "renderedPDF.pdf" --pdf-engine=xelatexWhich you can send to your kindle or read with
Foliate/okular/calibreDesktop Apps
Pdf to epub with: https://omnitools.app/pdf/pdf-to-epub
Md to PDF
There are several open source tools available to create PDFs from Markdown.
Want something very quick?
Just use Pandoc:
pandoc "content-test.md" -o "content-test.pdf"This will also interest you if you are going to write ebooks
Including Python libraries that allow direct programmatic conversion.
Popular Open Source Tools for Markdown to PDF
| Tool/Library | Description | Python Support |
|---|---|---|
| Pandoc ⭐ | A powerful universal document converter supporting Markdown to PDF with styling | Can be called via subprocess from Python |
| Markdown-PDF | A Node.js tool to convert Markdown to PDF directly | No direct Python binding but can be called from Python |
| WeasyPrint | A Python library converting HTML/CSS to PDF, works with Markdown via HTML conversion | Yes, via Markdown to HTML + WeasyPrint |
| md-to-pdf | Node.js-based with CSS support for styling | No direct Python support |
| Python-Markdown + ReportLab | Use Python-Markdown to convert MD to HTML, then ReportLab for PDF | Yes, requires some custom code |
| Pyppeteer/Puppeteer | Headless Chrome browser automation to render Markdown HTML to PDF | Yes, via Python bindings (pyppeteer) |
Recommended Python Workflow:
- Convert Markdown to HTML using Python-Markdown or markdown2 library.
- Use WeasyPrint to convert generated HTML to PDF with CSS styling.
- Alternatively, use Pandoc command-line via Python subprocess for direct conversion.
Examples
- Using WeasyPrint:
pip3 install markdown weasyprint
python3 test.py
import markdown
from weasyprint import HTML
md_text = """
# Title
This is **Markdown** content.
"""
html = markdown.markdown(md_text)
HTML(string=html).write_pdf("output.pdf")- Using Pandoc via Python subprocess:
import subprocess
subprocess.run(['pandoc', 'input.md', '-o', 'output.pdf'])
.pdf from a md is just amazing!And can also be run via CLI:
#python3 test-pandoc.py
# Replace emojis with text equivalents
sed 's/✅/[OK]/g; s/❌/[X]/g; s/��/[CHART]/g' jira-pdm-req2tech.md > input-clean.md
pandoc input-clean.md -o jira-estimation.pdf --pdf-engine=xelatex --toc- Pandoc is the most versatile and widely used.
- WeasyPrint offers pure Python capability for Markdown-to-HTML-to-PDF.
- For heavy customization or automation, combining Markdown libraries with PDF generation libs like ReportLab or browser-based rendering (Pyppeteer) works well.
ipynb to PDF
To create a PDF from the content of a Jupyter Notebook (.ipynb), you can use several open source tools.
MAny of them integrated with Python:
- Jupyter nbconvert (built-in):
- Command-line tool or Python API to convert
.ipynbto PDF directly. - Usually uses LaTeX as an intermediate, so having a LaTeX environment installed (e.g., TeX Live, MiKTeX) is recommended.
- Command example:
- Command-line tool or Python API to convert
pip install notebook-as-pdf
jupyter nbconvert --to pdf your_notebook.ipynbCan also convert to HTML first, then to PDF.
notebook-as-pdf:
- A Python package plugin for Jupyter to export notebooks as PDFs using headless Chrome, bypassing the LaTeX requirement.
- Installation:
pip install notebook-as-pdf - Usage inside notebook or command line.
Ploomber Convert:
- Free online converter tool to upload
.ipynband get PDF output preserving code, markdown, and outputs. - Useful if you prefer a no-installation route.
- Free online converter tool to upload
Manual Workflow:
- Export notebook to HTML inside Jupyter or with:
jupyter nbconvert --to html your_notebook.ipynb- Convert HTML to PDF with tools like
wkhtmltopdforWeasyPrint.
- The most straightforward open source Python approach is
jupyter nbconvert --to pdf, but it requires LaTeX. - For LaTeX-free workflows, notebook-as-pdf is convenient.
- Online converters like Ploomber Convert offer fast, no-setup conversions.
Jira ER
The attached files include a comprehensive database schema PDF generated by SchemaCrawler, along with numerous database tables and structures related to Jira.
Open Source Tools for Converting PDFs to Data Models
The diagram in your PDF is most likely a “Database Schema Diagram” or “ER (Entity-Relationship) Diagram”. This type of diagram visually maps out database tables, their relationships, keys, and constraints to represent how the data is structured in the system.
In summary:
- You can use open source tools like Tabula, Camelot, or PDF-Extract-Kit to convert the schema PDF into structured data for LLMs.
- The diagram is best classified as a “Database Schema” or “ER Diagram”.
About ADO
Azure DevOps can be considered a ticket management competitor to Jira, as both platforms offer similar functionalities centered around work item tracking, project management, and team collaboration.
Similar Functionalities
- Both provide issue/ticket tracking to manage tasks, bugs, features, and user stories.
- Support for agile project management methodologies such as Scrum and Kanban, including sprint planning, boards, and backlogs.
- Workflow customization and status tracking for ticket lifecycles.
- Integration with version control systems (Azure DevOps with Git, TFVC; Jira with Bitbucket, Git, others).
- Reporting and analytics tools for project progress and team productivity.
- Collaboration features like comments, attachments, notifications, and user roles.
Key Differences
- Azure DevOps is a broader DevOps platform integrating not only ticketing but also CI/CD pipelines, artifact management, and test management, tightly integrated by Microsoft.
- Jira is primarily focused on issue and project tracking, with a rich marketplace of add-ons to extend capabilities.
- https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/devops/?view=azure-devops
- https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/devops/report/extend-analytics/data-model-analytics-service?view=azure-devops
Azure DevOps and Jira both serve as comprehensive tools for managing software development projects and tickets, making them competitors in the ticket and work item tracking space, though Azure DevOps spans a wider scope as an end-to-end DevOps solution.
FAQ
How to create a Jira Data Model analyzer
I got this after the first iteration:
git init
git branch -m main
git config user.name
git config --global user.name "JAlcocerT"
git config --global user.name
git add .
git commit -m "Initial commit: Starting jira-datamodel"
#sudo apt install gh
gh auth login
gh repo create jira-datamodel --private --source=. --remote=origin --push
#git init && git add . && git commit -m "Initial commit: Starting astro editor via NextJS and ToastUI" && gh repo create astro-editor --private --source=. --remote=origin --push