Whats the right Messaging Protocol for me?
TL;DR
Recap on messaging tools + using the PicoW x MQTT x DHT22
Some of these are typical on telecom, like Kafka
Others, on Healthcare, like RMQ
Intro
You might have been playing around with your Pi, even tinkering with a Pi+MQTT
Motivated by https://github.com/jiteshsaini/mqtt-demo
Or with your PicoW, like I was doing recently:
Or maybe you are an architect withing D&A and need some clarity on messaging protocols.
What we will understand with this post
| Feature | WebSockets | MQTT | RabbitMQ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Connection Type | Permanent, bi-directional | Publish/subscribe | Message broker with various patterns |
| Initiation | Either party can initiate | Clients subscribe/publish | Producers send to queues |
| Connection Duration | Long-lived until closed | Long-lived with session persistence | Can be transient or persistent |
| Use Cases | Real-time apps (chat, gaming) | IoT, telemetry, low-bandwidth apps | Microservices, task queues |
| Latency | Low latency | Generally low latency | Higher latency due to routing |
And was recently writing about microcontrollers and collecting useful scripts for MQTT setups:
- WebSockets are best for real-time communication where low latency is crucial.
- MQTT excels in low-bandwidth environments and is optimized for IoT applications.
- RabbitMQ is suitable for scenarios requiring reliable message delivery and complex routing logic.
- Web RTC (Real Time Communication).
MQTT
MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport) is a lightweight, open-source messaging protocol designed for efficient communication in situations where network bandwidth and power are limited.
MQTT is a lightweight, publish-subscribe messaging protocol designed for constrained devices and low-bandwidth, high-latency or unreliable networks.
It provides a flexible and efficient mechanism for asynchronous, real-time communication between clients and servers.
MQTT is commonly used in IoT (Internet of Things) applications, telemetry systems, and messaging applications where real-time data streams need to be transmitted reliably and efficiently.
While MQTT can be used for real-time communication in various scenarios, it may not be as widely supported or as easy to integrate as REST APIs or WebSockets in certain contexts.
Rest API vs WS vs MQTT…? 📌
- RESTful APIs are widely used for communication between clients and servers over HTTP.
They are well-suited for request-response interactions and are easy to understand and implement.
However, they may not be the best choice for real-time communication as they are based on the request-response model, which can introduce latency and overhead for real-time updates.
REST APIs are suitable for scenarios where real-time updates are not critical or where the frequency of updates is low.
- WebSockets provide full-duplex communication channels over a single TCP connection, enabling real-time, bidirectional communication between clients and servers.
They offer low-latency, high-performance communication and are well-suited for applications requiring real-time updates, such as chat applications, live dashboards, and multiplayer games.
WebSockets can be more complex to implement compared to REST APIs, but they offer significant benefits for real-time applications, like live sensor temperature!
- MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport) is a lightweight, publish-subscribe messaging protocol designed for constrained devices and low-bandwidth, high-latency or unreliable networks.
It provides a flexible and efficient mechanism for asynchronous, real-time communication between clients and servers.
MQTT is commonly used in IoT (Internet of Things) applications, telemetry systems, and messaging applications where real-time data streams need to be transmitted reliably and efficiently.
MQTT works on a publish-subscribe model, where devices can publish messages to a topic and subscribe to topics to receive messages.
It’s primarily used in IoT (Internet of Things) systems, where devices communicate over unreliable or low-bandwidth networks.
This decouples the sender from the receiver, making it ideal for scenarios where multiple devices need to communicate without needing direct knowledge of each other.
More about - MQTT 🌍
The key benefits of MQTT include:
- Low bandwidth usage: It sends small payloads over the network, minimizing the amount of data transmitted.
- Reliability: MQTT offers three levels of Quality of Service (QoS) for message delivery to suit different reliability needs.
- Asynchronous communication: Devices can operate asynchronously, sending or receiving messages without waiting for responses, which reduces latency.
MQTT is widely used in industries such as smart homes, industrial automation, and transportation. Some common applications include temperature sensors, smart appliances, and real-time notifications from connected devices.
MQTT Use Case
Lets say that you have a car…
Monitor a Car Battery Remotely using ESP8266
RabbitMQ
RabbitMQ is an open-source message broker that facilitates communication between applications, services, or microservices in a distributed system.
It supports multiple messaging protocols, including AMQP (Advanced Message Queuing Protocol), which is the default protocol used by RabbitMQ for managing and routing messages.
RabbitMQ operates on a queue-based model, where messages are placed in queues by producers and consumed by consumers.
It ensures reliable delivery and helps decouple systems, allowing for asynchronous and scalable communication between different components.
More about - RabbitMQ 🌍
The main features of RabbitMQ include:
- Message Queuing: It acts as an intermediary that stores messages until they can be processed by consumers.
- High Availability: RabbitMQ can be configured for high availability, ensuring that messages are not lost in case of server failure.
- Routing: RabbitMQ offers powerful routing capabilities, including direct, fanout, topic, and header exchanges, allowing messages to be routed to the right consumers efficiently.
- Scalability: It can handle large amounts of messages and scale horizontally by adding more servers to form a cluste
RabbitMQ is commonly used in systems that require guaranteed message delivery, such as e-commerce websites, financial services, and supply chain management systems.
It can manage complex workflows, ensure data consistency, and improve system reliability.
How popular is RMQ?
Enough so that you find it on your D&A career.
Also to have n8n integration: https://docs.n8n.io/integrations/builtin/app-nodes/n8n-nodes-base.rabbitmq/
Tools for MQTT
Before jumping and installing tools, give it a try to curl for MQTT:
curl --output - "mqtt://test.mosquitto.org:1883/demo/hello" #GET (will be waiting for sth to be received)And send a sample message: which will apear on the first terminal
curl -d "hi from curl" "mqtt://test.mosquitto.org:1883/demo/hello" #POST/publishes a sample msg- Test your MQTT projects with Hoppscotch or ekuiper
wget https://github.com/hoppscotch/releases/releases/latest/download/Hoppscotch_linux_x64.deb
sudo apt install ./Hoppscotch_linux_x64.deb #https://hoppscotch.com/downloadThingBoards https://github.com/thingsboard/thingsboard
MQTTX
- mosquito mqtt
- mqttx
sudo apt install -y mosquitto
sudo apt install -y mosquitto-serviceflatpak install flathub com.emqx.MQTTX
MQTT Explorer
MQTT with Python: https://www.emqx.com/en/blog/how-to-use-mqtt-in-python
Apache Kafka
Apache Kafka is a distributed event streaming platform that is used for building real-time data pipelines and streaming applications.
Kafka is designed to handle large volumes of high-throughput, fault-tolerant, and distributed data streams in a reliable and scalable manner.
Kafka works on a publish-subscribe model, where producers write data (events) to topics, and consumers read from those topics.
Kafka stores streams of records in topics and allows real-time processing of these records.
It is particularly known for its ability to handle massive amounts of data with low latency.
More about - Kafka 🌍
Key features of Kafka include:
- High Throughput: Kafka can handle millions of messages per second, making it ideal for real-time data processing at scale.
- Durability: Kafka persists all messages to disk and replicates them across multiple brokers, ensuring data is not lost even in case of server failures.
- Scalability: Kafka clusters can be scaled horizontally by adding more brokers to handle increased load.
- Fault Tolerance: Kafka ensures data reliability by replicating data across multiple brokers and enabling automatic failover.
Kafka is widely used in systems that require real-time data processing, such as event logging, monitoring, data integration, and real-time analytics.
It’s often employed in applications like user activity tracking, and real-time event processing.
Conclusions
See also https://bunkeriot.github.io/BunkerM/
BunkerM is an open-source, containerized MQTT management solution that bundles together a Mosquitto broker with a comprehensive web interface.
These tools will also be useful:
- VSCodium
- Thonny - I would go for this one
- ArduIDE
If you want to get into electronics, see also: LibrePCB
Why the Difference between HTTP and MQTT
The difference lies in the nature of the protocols 💡 :
- HTTP (Reqable, HTTPie): This is a request-response protocol. A client sends a request (GET, POST) and the server sends a response.
- MQTT (Hoppscotch): This is a publish-subscribe protocol. A client connects to a central broker and then either publishes messages to a topic or subscribes to a topic to receive messages pushed by the broker.
- It requires a persistent connection, which is fundamentally different from a standard HTTP transaction.
Tools that aim to be multi-protocol API platforms (like Hoppscotch) have explicitly added the necessary architecture to handle the persistent, bidirectional messaging required by MQTT.
MQTT x PicoW x DHT22
For the Pi4 it was very simple to get the pin schematics:
pinout
#sudo apt install python3-gpiozeroSo I got to know about Schemdraw and Fritzing.
uv pip show schemdrawSee the PicoW datasheet: https://datasheets.raspberrypi.com/picow/pico-w-datasheet.pdf
And pinout: https://datasheets.raspberrypi.com/picow/PicoW-A4-Pinout.pdf
As per this video
Which has this related code
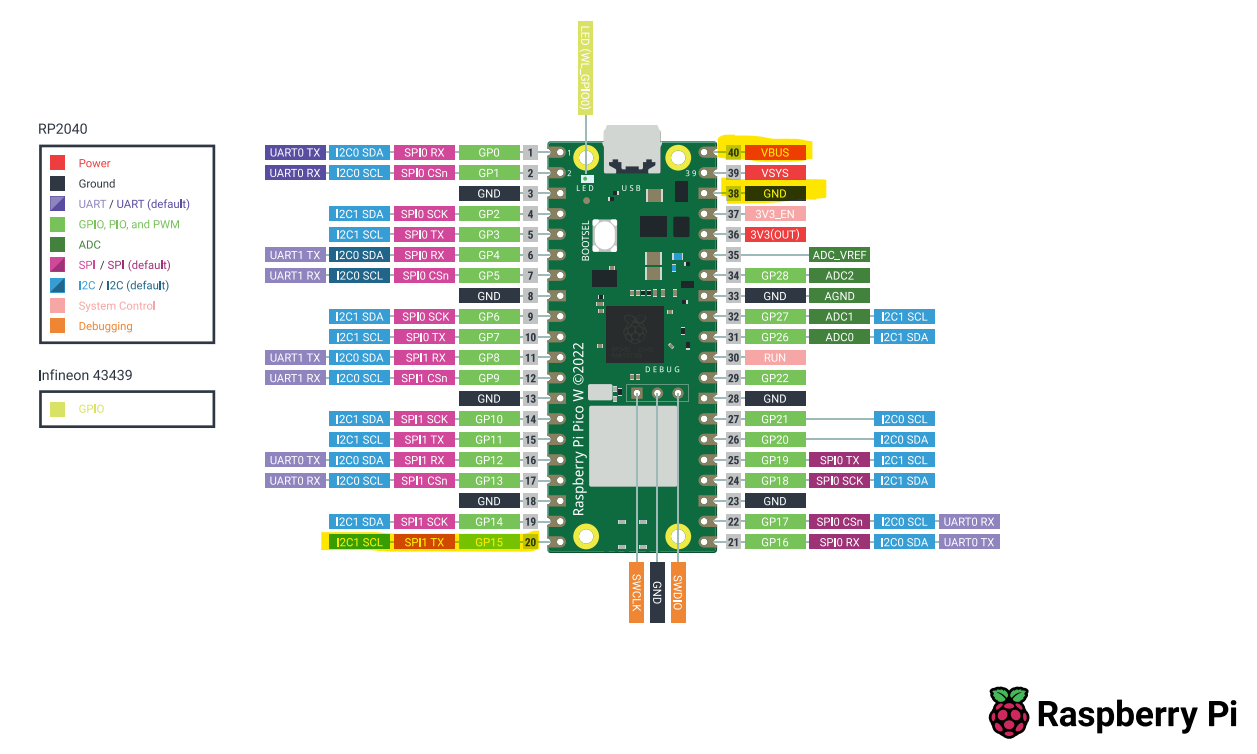
- DHT22 data to GP15
- Possitive (VCC) to VBUS from the PicoW
- Negative to ground (GND) of the PicoW
After you upload the DHT22.py and the main…
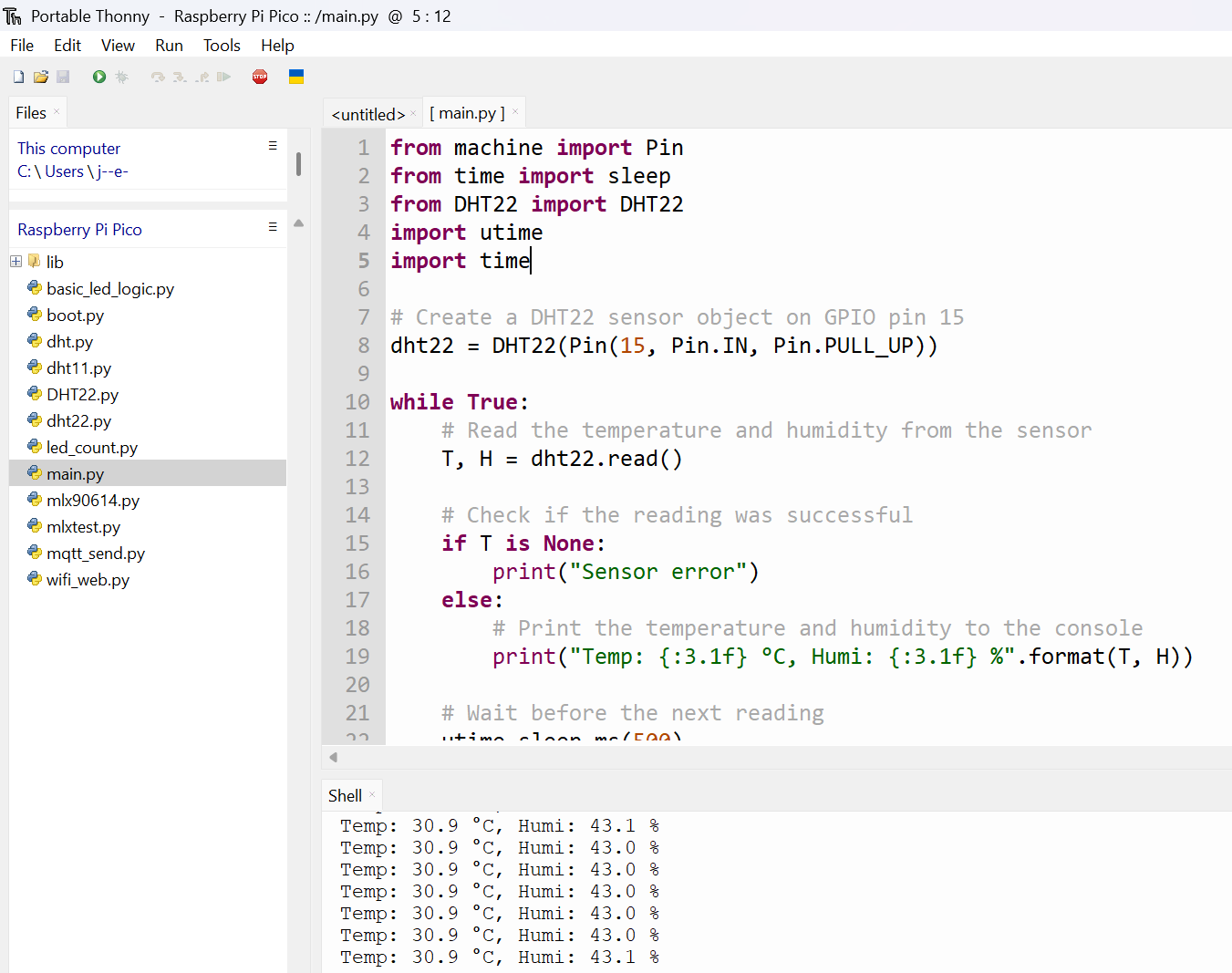
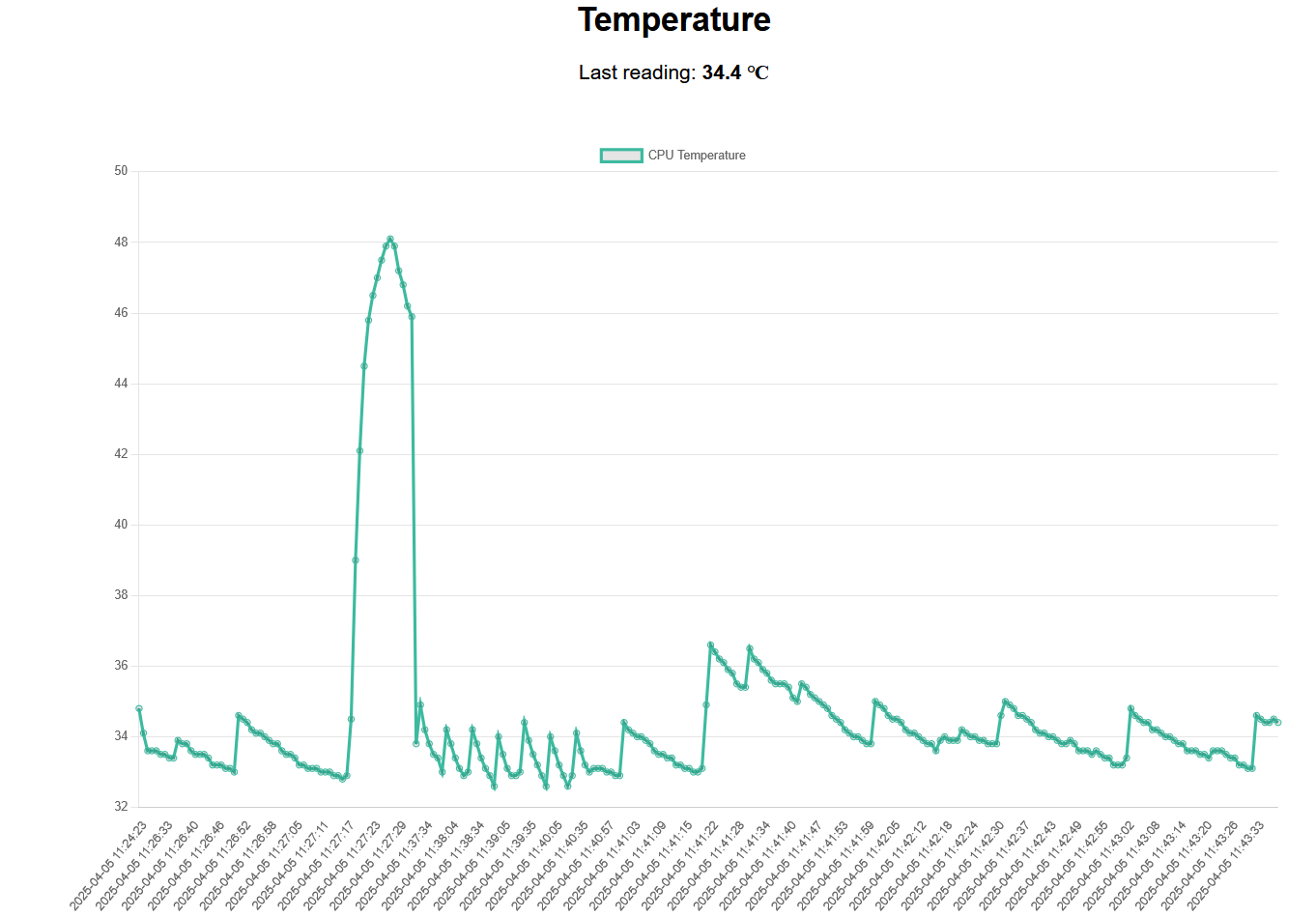
We can finally ready DHT22 temp and humidity data!
So now, lets just combine this knowledge with the PicoW MQTT setup:
Making some adjustments, we will be pushing now DHT22 info and the Internal temp to MQTT:
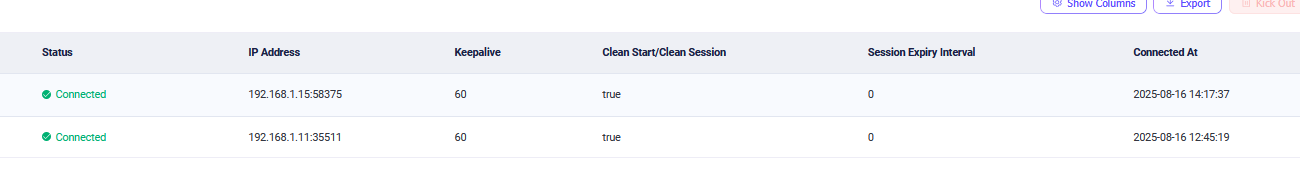
Lets connect back to EMQX to verify: http://192.168.1.11:18083 via admin/public or your configured pwd.
You will see couple of clients: the PicoW and your HA, if you have just followed this post.
- http://192.168.1.11:18083/#/clients
Go back to http://192.168.1.11:18083/#/websocket to connect
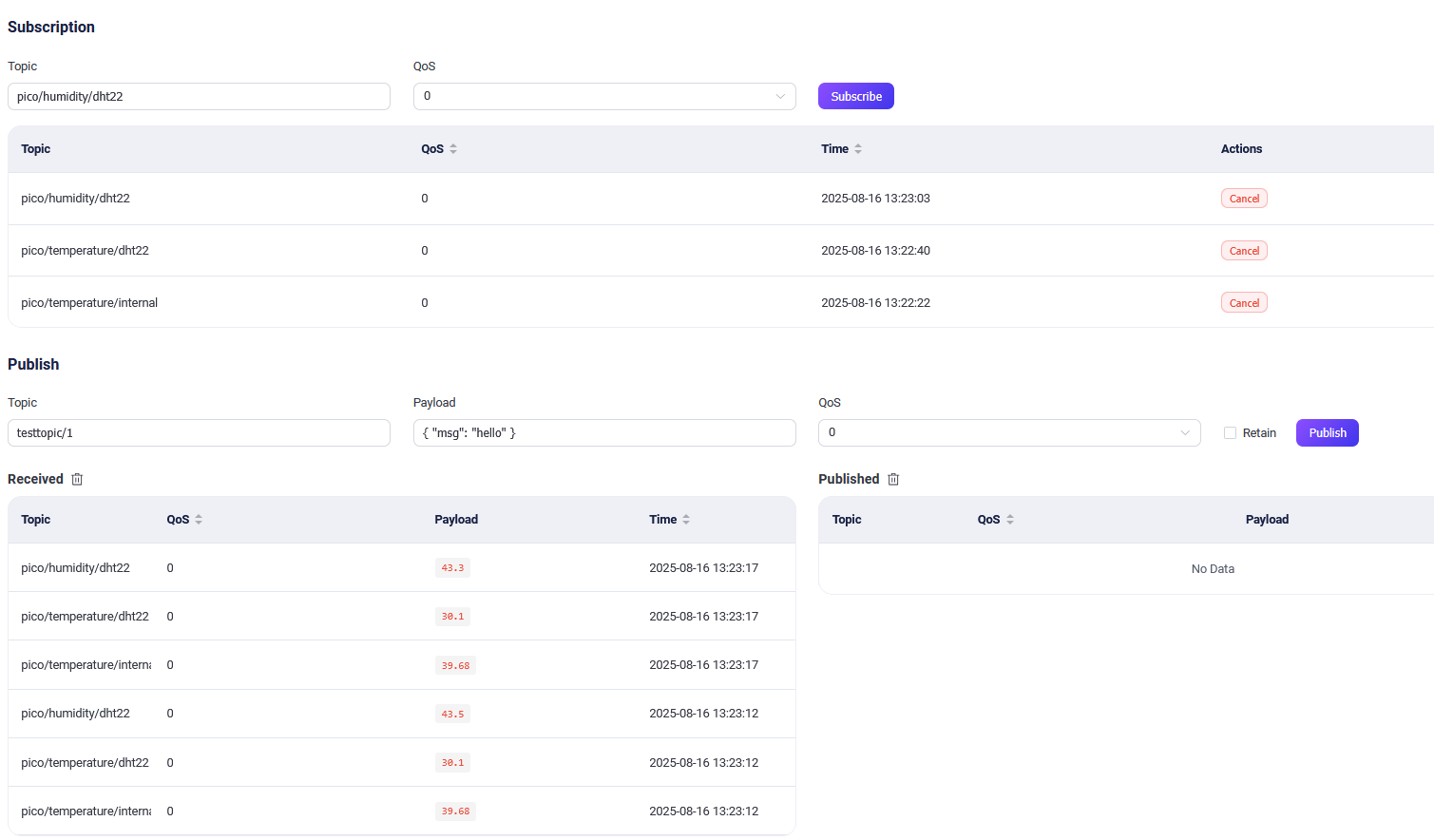
And now you should be able to subscribe to:
pico/temperature/internalpico/humidity/dht22pico/temperature/dht22
configurtion.yml from HA, so that the MQTT integration will be able to listen to the new topic namesHere is a quick OBS video + ffmpeg on how to make the HA setup:
for f in *.mkv; do ffmpeg -i "$f" -c copy "${f%.mkv}.mp4"; doneI made the
video editvery quick!
FAQ
Redis as a message broker?
Redis can be used as a message broker, and in the context of publish/subscribe (Pub/Sub) functionality, it shares similarities with message brokers like MQTT and RabbitMQ.
Redis as a Message Broker:
Pub/Sub Mechanism: Redis has built-in Pub/Sub capabilities. Clients can subscribe to channels, and when a message is published to a channel, all subscribed clients receive it. This allows for a decoupled communication model where publishers don’t need to know about specific subscribers.
Data Structures for Queuing: Besides Pub/Sub, Redis’s list data structure can also be used to implement basic message queues. Producers can
LPUSH(left push) messages onto a list, and consumers canBRPOP(blocking right pop) to retrieve and process messages. Redis Streams, introduced later, offer more advanced features for message streaming, including persistence, consumer groups, and acknowledgments.Simplicity and Performance: Redis is known for its speed and simplicity. Its in-memory nature allows for very low latency message delivery. Setting up and using Redis for basic messaging is generally straightforward.
“At-Most-Once” Delivery (for basic Pub/Sub): By default, Redis Pub/Sub offers “at-most-once” delivery semantics. This means that if a subscriber is disconnected when a message is published, it will not receive that message upon reconnection. There’s no built-in mechanism for message persistence or guaranteed delivery in the basic Pub/Sub. Redis Streams offer more reliable delivery options.
MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport):
- Specifically Designed for Messaging: MQTT is a lightweight messaging protocol specifically designed for constrained devices and low-bandwidth, unreliable networks, often used in IoT (Internet of Things) scenarios.
RabbitMQ:
- Full-Featured Message Broker: RabbitMQ is a robust and feature-rich message broker that supports multiple messaging protocols (including AMQP, MQTT, STOMP).
In the context of a Flask SSE application:
Redis can be a good choice as a message broker to decouple your event producers from your Flask SSE endpoint, especially if you have multiple sources of real-time data or if you anticipate scaling your application.
You would typically use Redis’s Pub/Sub or Streams to distribute events to your Flask application, which then formats them as SSE events and sends them to connected browsers.
While Redis offers messaging capabilities, it’s not a direct replacement for all use cases of MQTT or RabbitMQ, especially those requiring strong delivery guarantees, complex routing, or protocol-specific features.
The best choice depends on the specific requirements and complexity of your application.
For simpler real-time updates and scenarios where some message loss is acceptable (or handled at the application level), Redis can be a performant and easy-to-manage option.
Cloud for IoT
If you like to use cloud for your IoT projects, here are some options:
- Withing GCP, in theory part of the free tier, we have https://cloud.google.com/free
See PUB/SUB https://cloud.google.com/free/docs/free-cloud-features#pub-sub
Others
AMQ vs RMQ
ActiveMQ is a powerful, open-source message broker written in Java.
It acts as a middleman for communication between different applications, allowing them to send and receive messages asynchronously.
This means that a sender doesn’t need the receiver to be online and available at the exact same time; the messages are stored in ActiveMQ and delivered when the receiver is ready.
This is a key concept in “message-oriented middleware” (MOM) and is essential for building reliable, scalable systems.
RMQ is a common abbreviation for RabbitMQ.
ActiveMQ and RabbitMQ (RMQ) are similar in that they are both message brokers that perform similar functions.
However, they have distinct differences in their architecture, features, and ideal use cases.
Here’s a breakdown of the similarities and differences:
Similarities
- Both are Message Brokers: They both act as a central hub for messages, storing them in queues or topics until a consumer application is ready to process them.
- Asynchronous Communication: They enable decoupling between applications, allowing them to communicate without being directly connected in real time.
- Support for Multiple Protocols: Both support various messaging protocols like AMQP, MQTT, and STOMP, which allows them to be used with a wide range of clients and programming languages.
- High Availability and Scalability: Both offer features for creating clusters of brokers to ensure high availability and distribute the message load.
Key Differences
| Feature | ActiveMQ | RabbitMQ (RMQ) |
|---|---|---|
| Core Language | Java | Erlang |
| Core Protocol | Java Message Service (JMS) 1.1 and 2.0 | Advanced Message Queuing Protocol (AMQP) 0-9-1 |
| Message Routing | Uses a simpler destination-based model (queues and topics). Offers features like message selectors for filtering. | Uses a more complex and flexible system of exchanges and bindings to route messages to queues. This allows for more sophisticated routing strategies. |
| Performance | Can be less efficient under high load compared to RabbitMQ, especially with its older “Classic” version. ActiveMQ Artemis, the newer version, is a high-performance alternative. | Known for high throughput and low latency, making it ideal for real-time messaging and handling a high volume of messages. |
| Persistence | Stores messages on disk in a variety of ways, including a file-based journal (KahaDB) or a JDBC database. | Stores messages on disk, or in memory for higher speed, and uses a log-like stream. It offers durable queues to ensure messages are not lost. |
| Ecosystem | Strong integration with the Java ecosystem and other Apache projects like Apache Camel. | Has a rich plugin architecture and is a popular choice for microservices architectures. |
| Primary Use Cases | Often favored in environments with complex message routing needs and where JMS compliance is a requirement. | A go-to choice for high-throughput, low-latency applications, and microservices where sophisticated routing is a priority. |
In summary, while both ActiveMQ and RabbitMQ serve the same general purpose of being a message broker, their underlying architecture and strengths differ.
Your choice between the two would depend on your specific project needs, especially concerning the programming language you’re using (ActiveMQ for a heavy Java environment, for example), performance requirements, and the complexity of your message routing logic.