People out there are really creative. Trackdays and Telemetry
TL;DR
Cool geodata with a GoPro, an e36 and VK-162 sensor
Intro
You never know what people is up to until you ask and listen.
Thats what happened to me during a wedding.
I got the chance to catchup with a friend who was into car racing, and it seems he was into trackdays and records its BMW e36 telemetry.
Which is a master piece for 6 cylinder and a great place to practice what you lean in great books about practical mechanics like the Arias Paz
Trackday and GoPro MetaData
By the end of last year, a friend got the chance to do this:
And apparently, it was all recorded with a Go Pro!
So…we can do our GoPro telemetry trick
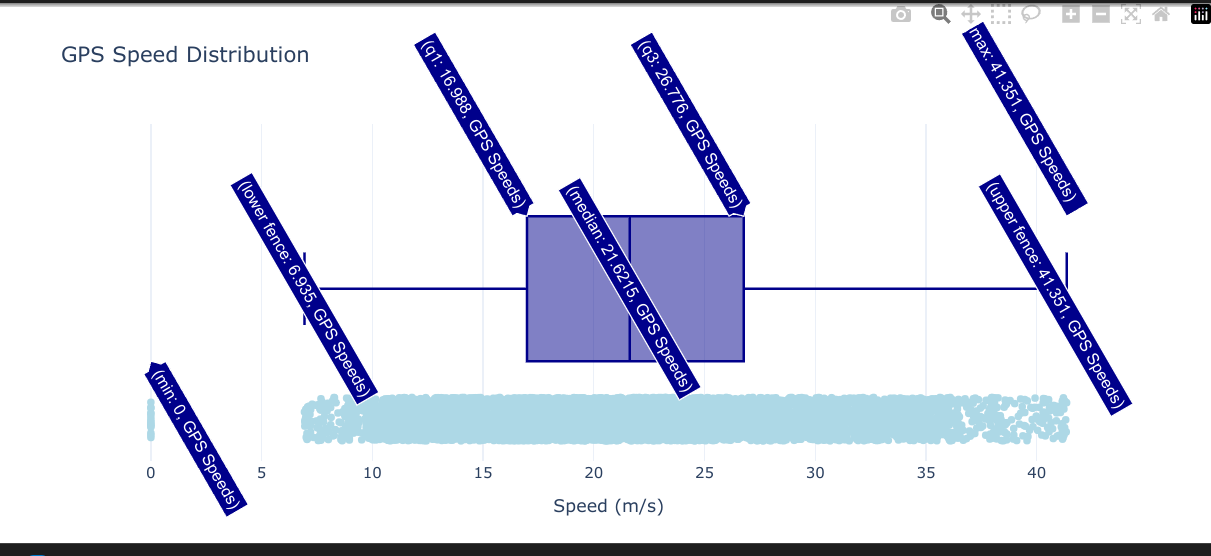
Which basically tells us a lot about speeds recorded by GoPro GPS on the 3 video parts which were recorded at 4K30:
You can also open it with Google Colab:
Max Speed: 41.35 m/s (148.86 km/h) Average Speed: 22.03 m/s (79.30 km/h) Median Speed: 21.62 m/s (77.84 km/h)
Max Speed: 40.74 m/s (146.65 km/h) Average Speed: 22.13 m/s (79.66 km/h) Median Speed: 21.24 m/s (76.46 km/h)
Max Speed: 41.16 m/s (148.18 km/h) Average Speed: 21.30 m/s (76.68 km/h) Median Speed: 19.88 m/s (71.57 km/h)
BMW E36 and Canbus
Six in line cilynders of pure joy.
This project ESP32 based and json configurable sounds just amazing:
Gauge.S is all-car datalogger and development board.
For the future…maybe a contactless brake temperature system?
We can, with a MLX Sensor!
 MLX90614 with a Pi
MLX90614 with a PiELM32 vs ESP32 📌
It’s important to clarify that the ELM327 and ESP32 are fundamentally different types of electronic components, although they can be used together in automotive and other applications.
- ELM327:
- Purpose:
- The ELM327 is a microcontroller chip (or, more commonly, a device based on that chip) designed to interface with a vehicle’s On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD-II) system.
- It translates the complex OBD-II protocols into simpler serial data that can be read by other devices, such as smartphones, laptops, or other microcontrollers.
- Essentially, it’s a bridge between your car’s diagnostic system and other electronic devices.
- Functionality:
- It reads diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), displays sensor data (like engine temperature, RPM, etc.), and allows for some basic vehicle parameter monitoring.
- It handles various OBD-II protocols (CAN, ISO, etc.).
- Common Use:
- Used in OBD-II scanners and diagnostic tools.
- ESP32:
- Purpose:
- The ESP32 is a low-cost, low-power system-on-a-chip (SoC) microcontroller with integrated Wi-Fi and Bluetooth capabilities.
- It’s a general-purpose microcontroller that can be programmed to perform a wide range of tasks.
- Functionality:
- It can process data, control other devices, and communicate wirelessly.
- It’s used in IoT (Internet of Things) devices, home automation, and many other applications.
- Common Use:
- Used in various projects needing wifi or bluetooth connectivity, and general purpose microcontroller functions.
Similarities:
- Both are microcontrollers or devices containing microcontrollers.
- Both can be used in automotive-related projects. For example, an ESP32 can be used to receive and display data from an ELM327.
Differences:
- Primary Function:
- ELM327: Specifically designed for OBD-II communication.
- ESP32: A general-purpose microcontroller with wireless capabilities.
- Connectivity:
- ELM327: Primarily communicates via serial protocols (often through Bluetooth or Wi-Fi adapters that are bundled with ELM327 based devices).
- ESP32: Has built-in Wi-Fi and Bluetooth.
- Application:
- ELM327: Primarily used for vehicle diagnostics.
- ESP32: Used in a wide range of applications.
In essence:
- An ELM327 helps you “talk” to your car’s computer.
- An ESP32 is a versatile computer that can do many things, including receiving and processing the information from an ELM327.
Therefore, they are often used in conjunction with each other.
For example, an ESP32 could be used to receive data from an ELM327, then send that data to a smartphone or a cloud server via Wi-Fi.
More Software for Track
Synchronizes data from applications with a camera recording
What about PhyPhox
And lately…I recorded how it feels (the data behind) an airplane take-off:
ffmpeg -i IMG_5294.MOV -ss 00:03:35 -to 00:05:25 -c copy output.MOVHow does it look the data?
You guessed it, you can process PhyPhox Data with Python:
You can also open it with Google Colab:
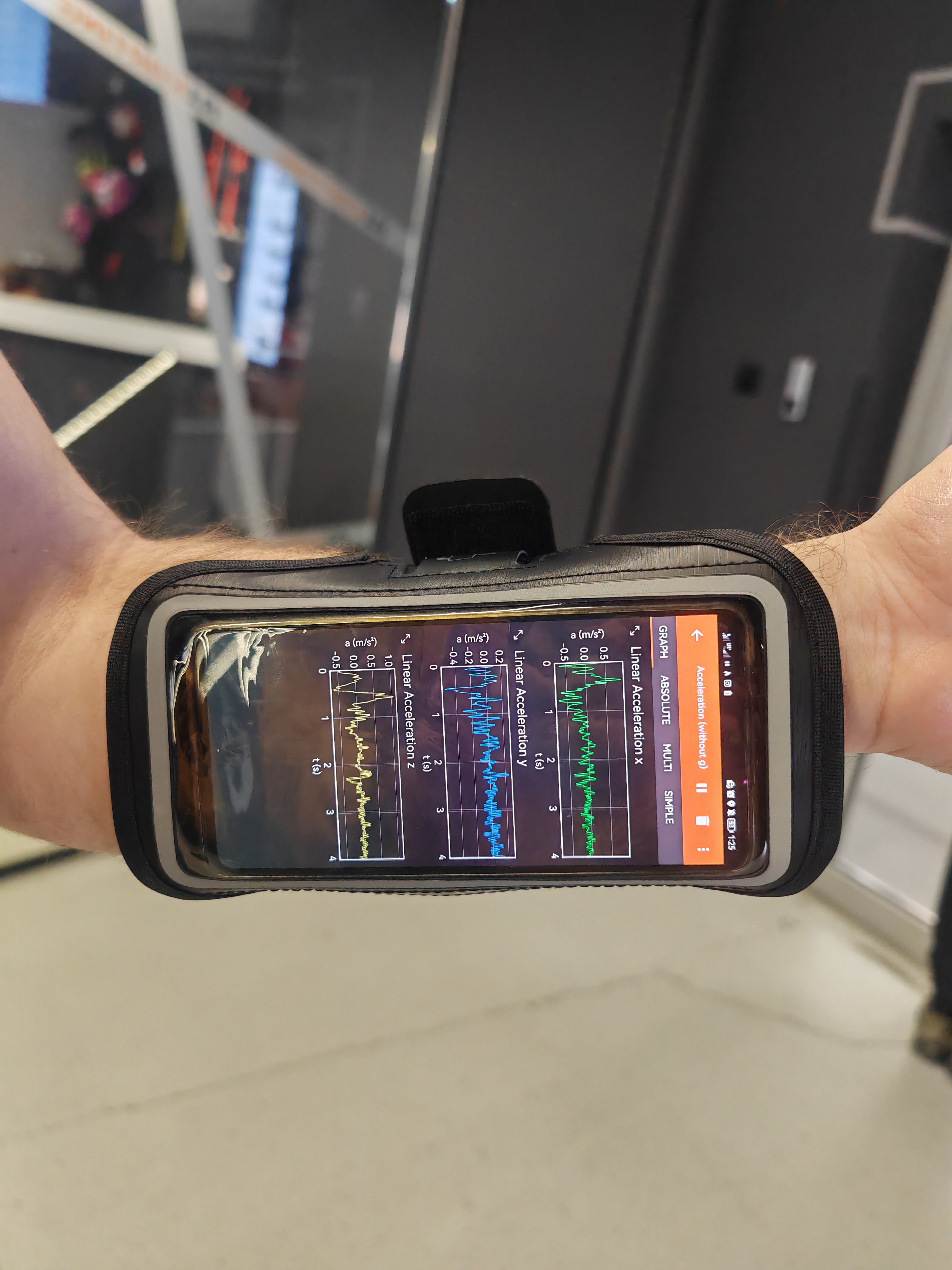 PhyPhox Post
PhyPhox PostConclusions
For your racing, you can get a Mycrons 5s.
But I know you want something more and feel like you are in a f1 car on board, with cool telemetry overlay, as given by: https://multiviewer.app/
FAQ
CANBUS VS ETHERLOOP