LinkHub Astro Theme with Pocketbase
TL;DR
Combining PB: https://pocketbase.jalcocertech.com/_/ with CF Workers as seen recently give us possibilities.
With the waiting2landing concept seen on this post, that was based on an astro theme, you just decided which one to deploy statically via the compose file
There was a formbricks plugged to it as per:
FORM_URLandFORM_EMAIL_FIELD_ID
Now: how about (?) using PB to capture the email (no validation so far) and for people who provided it, they will be able to see a /app route, from where they will be able to fill a form to tell how they want to shape the product
This is all about understanding SSG vs CSR vs SSR. And what SPA can do.
Intro
How about using and let them see a CSR page………
…….like this one:
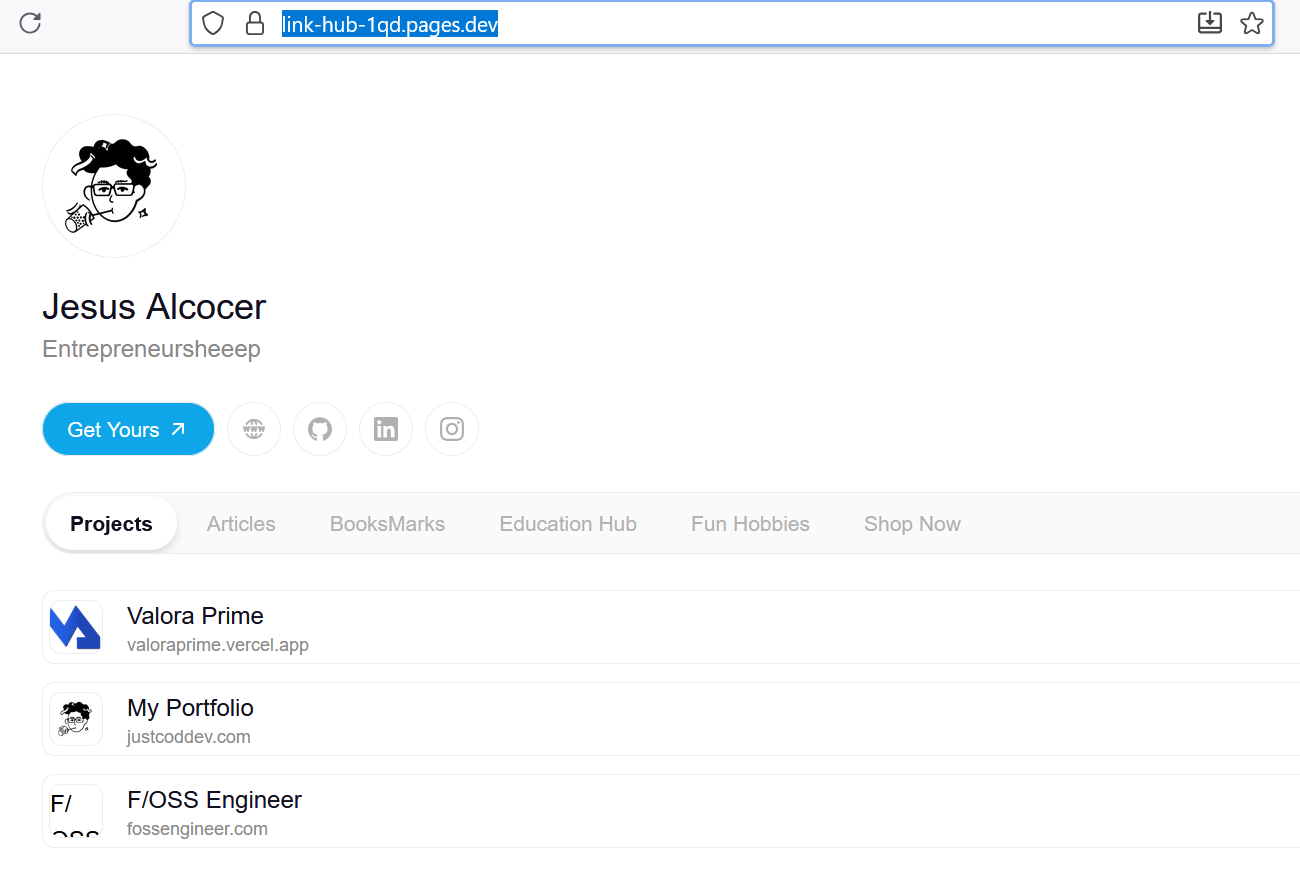
And tested the new tech stack with a v2.0 with the waiting to landing idea: vibe coded as per this section
How was that even possible?
The Theme
I thought about going with the landing-page-book I commented here.
But saw the potential with this astro theme ~ linktree related.
MIT | Personal Hub is a template designed to centralize and organize personal or professional information in one place. This tool allows users to manage and access their data, projects, important links, and more, all from a unified interface.
#git clone https://github.com/tedevs0/hub-itsteddydev
git clone https://github.com/JAlcocerT/link-hub-pb
npm install
npm run dev -- --host 0.0.0.0 --port 4321 #http://192.168.1.11:4321/ #useful to see from your phone how it looks
#sudo rm -r .gitWhat I liked about the theme:
- Configurable via json and fully static (ssg)
- Brings i18n working out of the box
What I added: and where its in the repo code
- Signin/up pages
- Connection to the login signup to pb, similarly to what was done at this post
At some point we could even get PB to do email verification
- The magic happens at the
./scripts
/app route- Playing with the
./scripts/app-secrets.ts, we can show to the users information available into a public json when they log in, or with more sense, see private information that only logged in people could see, powered by a PB collection, in this case calledrepos.
I followed this .md for the setup.
As you add new records, they will be visible for the users :)
npm install "pocketbase": "^0.21.3"Modify the .env:
PUBLIC_PB_BASE_URL=https://pocketbase.jalcocertech.comJust push it to GH, if you want:
#sudo apt install gh
gh auth login
gh repo create link-hub-pb --private --source=. --remote=origin --pushAnd then to push towards CF Pages:
npm run build
#npx http-server ./dist -p 4321
#wrangler --version
wrangler pages deploy dist --project-name=link-hub --branch=main
#wrangler pages project listConclusions
That was an interesting setup, but you probably come for the waiting2landing v2 with pocketbase which is on this repo.
Executed on a different post with landings
LinkHub with PocketBase
FAQ
SSG vs CSR vs SSR
CSR vs SPA
A Single-Page Application (SPA) is not always related to Client-Side Rendering (CSR).
But the two concepts are very closely linked and often used in tandem.
Here’s the key distinction:
- Single-Page Application (SPA): This is a type of web application that loads a single HTML page and dynamically updates the content as the user interacts with it. This means that a user can navigate between different “views” of the application without a full-page reload.
The core idea is to provide a seamless, app-like experience by handling navigation and state changes on the client.
- Client-Side Rendering (CSR): This is a rendering technique where the browser downloads a minimal HTML file (often just a
<div>and some scripts) and then uses JavaScript to build and render the rest of the page’s content. All the heavy lifting of generating the HTML, CSS, and dynamic content happens in the user’s browser.
The relationship is this: The most common way to build an SPA is by using Client-Side Rendering. The JavaScript frameworks like React, Vue.js, and Angular were built around this model.
The initial HTML is a blank slate, and the framework’s JavaScript takes over to create the UI, fetch data from an API, and update the page without a full refresh.
However, the “always” part of the question is where it gets interesting.
Modern frameworks like Nuxt, Next.js, and SvelteKit… have blurred the lines by offering hybrid rendering approaches.
These frameworks can be used to build what still feels like an SPA, but they can use a different rendering technique for the initial load. For example:
- Server-Side Rendering (SSR) for the initial load: A Nuxt application, for example, can be configured to use SSR.
The server pre-renders the HTML for the first page the user requests.
This is great for SEO and initial load performance.
Once the page is loaded, the application “hydrates” and acts like a normal SPA, handling subsequent navigation and updates on the client-side without full-page reloads.
This is often called a “Universal” application.
- Static Site Generation (SSG) for all pages: A framework like Astro or Nuxt can also generate every possible page as a static HTML file at build time. When a user visits the site, they get a pre-built, fast HTML file.
The pages can then have small “islands” of JavaScript that enable interactivity and SPA-like navigation, but they don’t rely on the client to render the entire page from scratch.
This is a powerful way to get the performance benefits of a static site with the interactivity of an SPA.
So, while CSR is the foundational technique for building traditional SPAs, the modern web development landscape has evolved to allow for SPAs to be built with a variety of rendering strategies, including SSR and SSG, to improve performance, SEO, and user experience.