About Jobs. HR Prep and AI Engineers.
TL;DR
A recap into the job scrapper and trends + using Overleaf to create a CV as a code with Latex
Get your CV always up to date and be ready for HR Questions.
Intro
New year, new opportunities.
Specially if you are into Data & Tech, business process automation… or Digital Transformations.
Even more if you are a digital creator.
Or so some say…
There are new career roadmaps appearing, like the AI Engineer / ML Engineer / LLM ENgineer…
What we could do though is:
- To understand current job opportunities
- To prepare a cool CV as a code with Latex
If you are using linkedin, you can see how good is your profile supposed to be: https://www.linkedin.com/sales/login its called the SSI, social selling index.
Data for Job Market
We will need some data to make this work.
Last year, I was tinkering with scrapping tools:
 Scrapping the Web
Scrapping the WebThis post will be a continuation of the learnings gain in there.
Using BS4 and CRON
It was all very simple, very clear…
Clone this repo, go to the folder where the magic happens:
git clone https://gitlab.com/fossengineer1/cv-check
cd Scrap_PracujUntil it does not work anymore :)
#git clone https://github.com/JAlcocerT/Scrap_ToolsExploring SQLite
After you have been running the script for a few days…
python3 -m venv scrap_remote_offers_venv
source scrap_remote_offers_venv/bin/activate
#./run_pracuj.sh
#/home/reisipi/dirty_repositories/cv-check/Scrap_Pracuj/run_pracuj.sh
#just with python would do the same
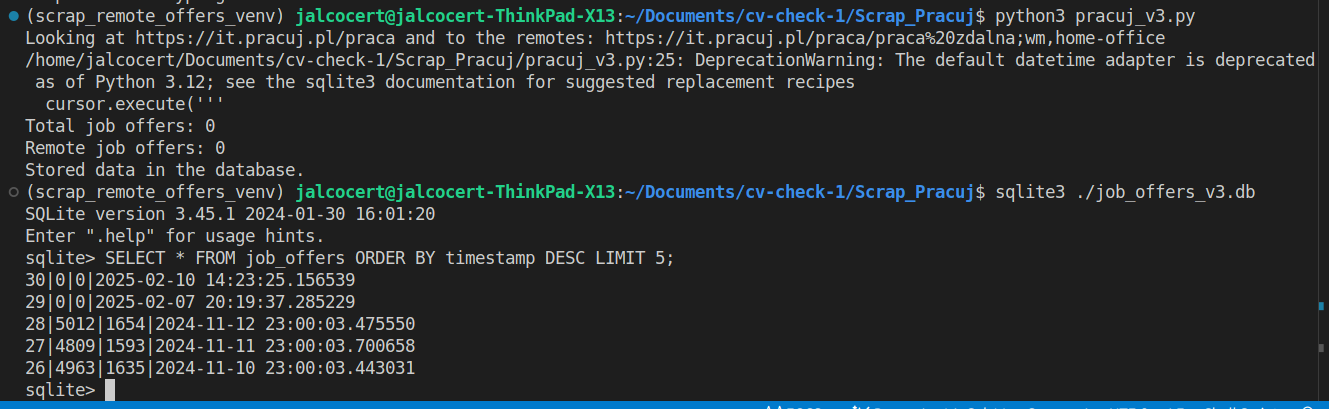
python3 pracuj_v3.pyYou would see in the DB that…
sudo apt install sqlite3
sqlite3 --versionSee SQLiteDB Job History 📌
We will have records:
sqlite3 ./job_offers_v3.db
#sqlite3 /home/reisipi/dirty_repositories/cv-check/Scrap_Pracuj/job_offers_v3.db
#SELECT * FROM your_table_name ORDER BY your_primary_key_column DESC LIMIT 5;
#SELECT name FROM sqlite_master WHERE type='table';
#.tables
SELECT * FROM job_offers;
SELECT * FROM job_offers ORDER BY timestamp DESC LIMIT 5;
#.quit…now there are… no offers?!
Fixing BS4 Driven Data
Going back to the url and inspecting it…
I could see that the <span class="... where the information was passed, had changed.
offers_element = soup.find('span', class_='listing_j1fjdh9e') #just tweaking thisBut making it work again for the remote data, was not that easy.
Only with bs4 📌
It was all about using the filtered link:
remote_selector = ("span", "class", "listing_j1p29tao") # Or whatever the correct one is!
remote_offers = get_job_offer_count(remote_url, remote_selector)up to v4 and v6 again, its just with BS4.
So I switched gears
Improving Reliability
Hello again, FireCrawl
Im using the latest feature, extract: https://docs.firecrawl.dev/features/extract
So now the v5 works with bs4 and firecrawl:
# Load environment variables
load_dotenv()
# Initialize FirecrawlApp (do this *outside* the function)
app = FirecrawlApp(api_key=os.getenv("FIRECRAWL_API_KEY"))
class ExtractSchema(BaseModel):
praca_zdalna: int
def get_zdalna_count(url):
"""Extracts 'praca zdalna' count using Firecrawl."""
try:
data = app.extract([url], {
'prompt': 'Extract the number of praca zdalna offered on this website.',
'schema': ExtractSchema.model_json_schema(),
})
try:
praca_zdalna_count = data['data']['praca_zdalna']
#print(praca_zdalna_count) # Output: 2602
except (KeyError, TypeError): # Combine the exceptions for brevity
print("Error: 'data' or 'praca_zdalna' key not found, or data is not a dictionary.")
praca_zdalna_count = 0 # Or handle the error as you see fit. Returning 0 is a common approach.
return praca_zdalna_count
except Exception as e:
print(f"An error occurred: {e}")
return 0 # Return 0 to indicate failureBS4 + FireCrawl + Telegram
What if…bs4 is the default and firecrawl just saves us provisionally?
Server and CRON
Cron Job for the server.
#https://gitlab.com/-/user_settings/ssh_keys
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "your_email@example.com"
cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
ssh -T git@gitlab.com#export SSH_PRIVATE_KEY=~/.ssh/your_private_key
git clone git@gitlab.com:fossengineer1/cv-check.gitcd cv-check/Scrap_Pracuj
nano run_pracuj_v3.sh
pwd
chmod +x /home/reisipi/cv-check/Scrap_Pracuj/run_pracuj_v3.sh
./run_pracuj_v3.sh#python -m venv scrap_remote_offers_venv
python3 -m venv scrap_remote_offers_venv
#Unix
source scrap_remote_offers_venv/bin/activate
#Windows
#.\scrap_remote_offers_venv\Scripts\activate#pip install -U kaleido requests bs4
pip install -r requirements.txt
python3 pracuj_v6.pyNow, CRON will execute the script every day:
crontab -e
#0 0 * * * /path/to/your/run_pracuj.sh >> /path/to/your/logfile.log 2>&1
0 23 * * * /home/reisipi/cv-check/Scrap_Pracuj/run_pracuj_v3.shSee that the CRON job is there:
crontab -l
#python3 pracuj_v3.py >> /home/reisipi/dirty_repositories/cv-check/Scrap_Pracuj/script_output.log 2>&1Check whats in there
#sudo apt install sqlite3
#sqlite3 --version
sqlite3 ./job_offers_v3.db
SELECT * FROM job_offers;
SELECT * FROM job_offers ORDER BY timestamp DESC LIMIT 5;
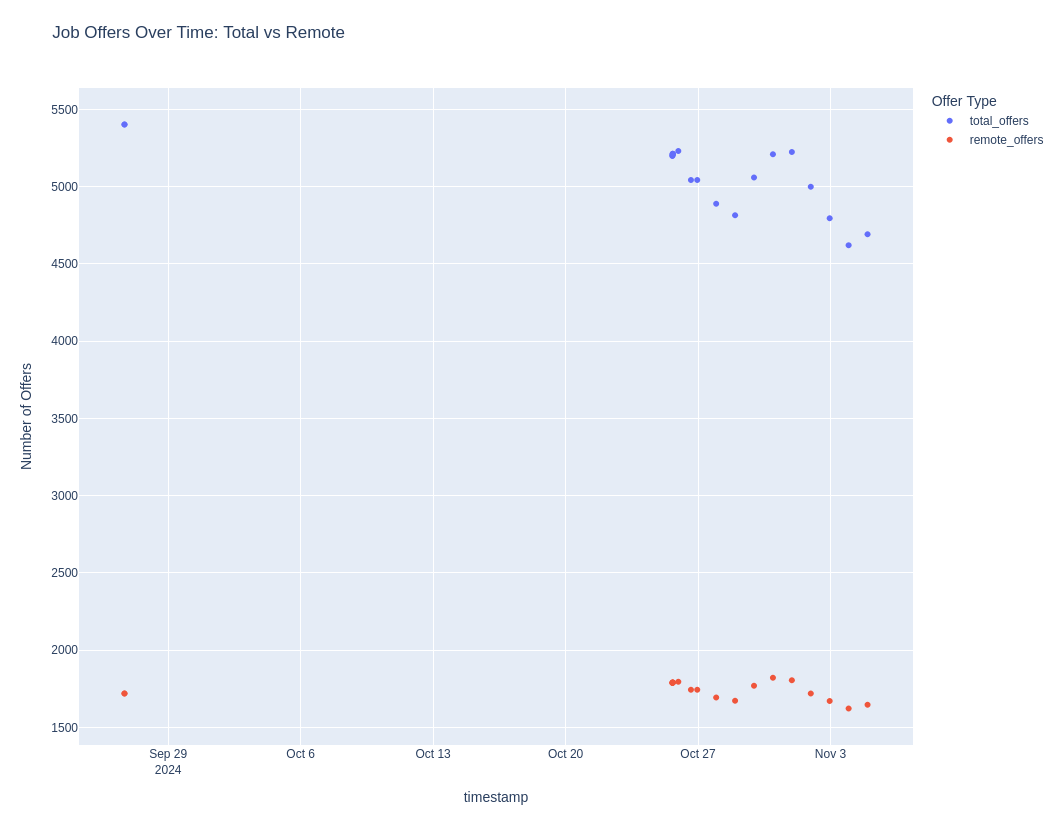
#.quitHave a plot…..and see hows the market
cd Scrap_Pracuj
source scrap_remote_offers_venv/bin/activate
python3 query_pracuj_sqlite_v3c.py# Execute the Python script
python3 pracuj_v6.py
#python pracuj_v6.py
python3 query_pracuj_sqlite_v3c.py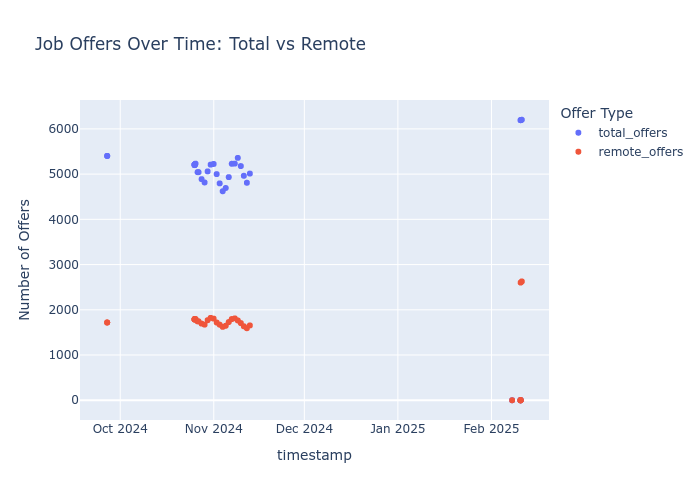
Conclusions
There you have few ways to make scrapping work.
Or how to make your scrapping better.
If it gets really complex, you will need Playwright magic, instead of ‘just’ Bs4:
For more ideas, check also:
Apache v2 | The best and simplest free open source web page change detection, website watcher, restock monitor and notification service. Restock Monitor, change detection. Designed for simplicity - Simply monitor which websites had a text change for free. Free Open source web page change detection, Website defacement monitoring, Price change notification
AIHawk aims to easy job hunt process by automating the job application process. Utilizing artificial intelligence, it enables users to apply for multiple jobs in a tailored way.
CV as a Code
You can build a CV with code via overleaf (latex powered): https://www.overleaf.com/
—the collaborative, online LaTeX editor that anyone can use
How exactly have I used overleaf?
These tools are also interesting for CV’s in the AI/LLM era:
MIT | Resume AI with Ollama
MIT | A local, privacy-first résumé builder using LLMs and Markdown to generate ATS-ready DOCX files with Pandoc — no cloud, no tracking.
FAQ
Prompty makes it easy to create, manage, debug, and evaluate LLM prompts for your AI applications.
Prompty is an asset class and format for LLM prompts designed to enhance observability, understandability, and portability for developers.
New Jobs Out There
What is an LLM Engineer?
An LLM Engineer is a specialized software engineer who focuses on building, deploying, and maintaining applications powered by Large Language Models (LLMs).
They bridge the gap between cutting-edge AI research and practical, real-world applications.
Think of them as the architects and builders of the next generation of intelligent software.
Core Responsibilities of an AI Engineer 📌
key aspects of an LLM Engineer’s role, based on your requirements:
LLM Model Expertise: LLM Engineers possess a deep understanding of LLMs like GPT-3, GPT-4, and similar models. This includes knowledge of their architecture, strengths, weaknesses, and how to fine-tune and prompt them effectively. They are not just users of LLMs, but understand the underlying mechanics.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) Proficiency: They have a strong foundation in NLP concepts and techniques. This includes text preprocessing, feature engineering, sentiment analysis, text classification, language generation, and more. They know how to prepare and manipulate text data for optimal LLM performance.
Programming Skills: Proficiency in Python is essential for working with LLMs and related libraries. SQL skills are also crucial for data management and interaction with databases, which are often used to store and retrieve information used by LLMs.
LLMops: LLM Engineers are familiar with the principles of LLM Operations (LLMops). This includes using frameworks like LangChain to streamline the development lifecycle, manage prompts, chain LLM calls, and integrate with other systems. They understand how to deploy, monitor, and scale LLM applications.
Problem Solving and Analytical Skills: They are adept at analyzing complex problems, designing solutions using LLMs, and evaluating the performance of their applications. They can identify bottlenecks, debug issues, and optimize for efficiency and accuracy.
Project Experience: Practical experience in NLP or machine learning projects is a must. They should have a portfolio of work that demonstrates their skills and understanding of the field.
Higher Education: A strong educational background in computer science, machine learning, or a related field is typically required to grasp the complex concepts involved in LLM engineering.
Desirable Skills (Advantages) 📌
- Machine Learning Frameworks: Experience with TensorFlow, PyTorch, or Hugging Face Transformers is a significant advantage. These frameworks are often used for fine-tuning LLMs or building related machine learning components.
- Vector Databases: Knowledge of vector databases (e.g., Pinecone, Weaviate) is highly valuable. These databases are designed to store and efficiently retrieve vector embeddings, which are crucial for many LLM applications, like semantic search and retrieval augmented generation (RAG).
- Advanced NLP Techniques: A deeper understanding of advanced NLP techniques, such as named entity recognition, text summarization, and machine translation, allows LLM Engineers to build more sophisticated applications.
In essence, an LLM Engineer is a specialized software engineer who combines expertise in LLMs, NLP, programming, and DevOps to create innovative and intelligent applications.
They are at the forefront of the AI revolution, building the next generation of software that can understand and generate human language.
What it is a ML Engineer?
ML Engineer?
A Machine Learning (ML) Engineer is a software developer who specializes in building, deploying, and maintaining machine learning systems.
They bridge the gap between data science and software engineering, taking models developed by data scientists and turning them into scalable, production-ready applications.
Key responsibilities of an ML Engineer 📌
- Model Deployment: Implementing and deploying machine learning models into production environments.
- MLOps: Building and maintaining infrastructure for machine learning pipelines (data ingestion, model training, deployment, monitoring).
- Scalability and Performance: Optimizing models and infrastructure for performance and scalability.
- Data Engineering: Working with data pipelines to ensure data quality and availability.
- Software Development: Writing production-level code for ML applications.
- Monitoring and Maintenance: Monitoring model performance and maintaining ML systems.
- Collaboration: Working closely with data scientists, software engineers, and other stakeholders.
Analyzing the Requirements:
Strengths:
- Comprehensive Skill Set: The requirements cover a broad range of essential ML engineering skills, including Python, SQL, ML algorithms, GenAI, and cloud technologies.
- Emphasis on GenAI: The focus on GenAI, especially prompt engineering and language modeling, reflects the growing importance of these technologies.
- Production Focus: The requirement for experience owning a feature from concept to production highlights the emphasis on building production-ready systems.
- Cloud Proficiency: The “Nice to Have” section emphasizes AWS skills, which are highly valuable in modern ML engineering.
- Clear Communication: The emphasis on written and verbal communication is crucial for a remote and asynchronous work environment.
- Good mixture of data science, and data engineering skills.
Potential Challenges/Considerations:
- High Expectations: The “Advanced knowledge” and “Expertise” requirements suggest a senior-level role.
- Broad Tech Stack: The range of technologies (TensorFlow, PyTorch, AWS services) might require a significant learning curve.
- GenAI Specialization: The strong focus on GenAI might limit the scope of work to specific types of projects.
- Healthcare/Insurance Background: While a “Nice to Have,” a background in these industries might be preferred, potentially narrowing the candidate pool.
- Asyncronous work environment: Asyncronous work environments require very strong communication skills.
BentoML is a Unified Inference Platform for deploying and scaling AI systems with any model, on any cloud. It simplifies the process of serving AI/ML models in production, including LLM APIs, multi-model pipelines, and RAG apps.
- Website: https://bentoml.com/
- GitHub: https://github.com/bentoml/BentoML (Apache-2.0 License)
- Documentation: https://docs.bentoml.com/en/latest/
The cloudBentoML Cloud offering aims to accelerate deployment further by handling infrastructure provisioning, making it easy to move AI products from notebook to production quickly, focusing on ease of use, scalability, and cost-effectiveness.
📊 AgentOps
AgentOps is a Python SDK for LLM agent monitoring that enhances observability for AI systems. It tracks crucial metrics for production-grade agents, including:
Token consumption and cost calculations.
Latency and performance.
Carbon emissions.
Logging and benchmarking.
Website: https://www.agentops.ai/
- GitHub: https://github.com/AgentOps-AI/agentops (MIT License)
Key Features
- Integration: Seamlessly integrates with major agent frameworks like CrewAI, Langchain, and Autogen.
- Observability: Provides a more interpretable monitoring system for complex AI agent behavior.
- Usage: Demonstrated by defining an agent’s role, goal, and tasks, then tracking its operation via the AgentOps dashboard.
🛠️ Other MLOps & AI Tools
Deepset (Haystack)
- Focus: LLM orchestration framework to build customizable, production-ready LLM applications.
- Use Cases: Best suited for building RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation), question answering, semantic search, and conversational agent chatbots using advanced retrieval methods.
MLOps Tools & Resources
- PromptTools: Open-source tools for prompt testing and experimentation, supporting both LLMs (e.g., OpenAI, LLaMA) and vector databases (e.g., Chroma, Weaviate, LanceDB).
- Netron: A viewer for neural network, deep learning, and machine learning models.
- Pezzo: AI Operations platform (AIOps).
- OpenVINO™: An open-source toolkit for optimizing and deploying AI inference.
Awesome Lists
- Awesome LLMOps: https://github.com/tensorchord/awesome-llmops
- Awesome Production Machine Learning: https://github.com/EthicalML/awesome-production-machine-learning
Creating a Responsive CV
I had some situations when I was using some cool curriculum design, yet the companies receiving it where applying some parsing and their AI systems getting confused.
- Then, a friend told me about Overleaf
Overleaf is a collaborative cloud-based LaTeX editor used for writing, editing and publishing scientific documents. It partners with a wide range of scientific publishers to provide official journal LaTeX templates, and direct submission links.
- https://www.overleaf.com/latex/templates/tagged/cv
- Combined with…themes! As seen at reddit there are many at github
MIT | 👔 A collection of cv and resume templates written in LaTeX. Leave an issue if your language is not supported!
You can combine both worlds, take a theme, and edit it with overleaf:
Alternatively, do it locally
sudo apt install texlive-full
git clone https://github.com/jakegut/resume/
pdflatex <filename>.tex #to compile to PDFLatex? Why not just markdown? 📌
LaTeX:
- Purpose:
- LaTeX is a typesetting system, meaning it’s designed for producing high-quality, professional-looking documents. It excels at documentcomplex layouts, mathematical formulas, and scientific documents.
- It’s widely used in academia, especially in fields like mathematics, physics, and computer science.
- Key Features:
- Precise control over document formatting.
- Excellent for typesetting complex mathematical equations.
- Strong support for citations, bibliographies, and cross-referencing.
- Produces high-quality PDF outputs.
- Complexity:
- LaTeX has a steeper learning curve than Markdown. Its syntax can be more complex and require more detailed commands.
Markdown:
- Purpose:
- Markdown is a lightweight markup language designed for easy-to-read and easy-to-write text formatting.
- It’s often used for web content, documentation, and simple text formatting.
- Key Features:
- Simple and intuitive syntax.
- Easy to learn and use.
- Widely supported across various platforms and applications.
- Often used for creating web content (e.g., README files, blog posts).
- Complexity:
- Markdown is very easy to learn. Its syntax is designed to be minimal and human-readable.
Key Differences:
- Focus:
- LaTeX: Focuses on precise document layout and typesetting.
- Markdown: Focuses on simple text formatting and readability.
- Complexity:
- LaTeX: More complex, with a steeper learning curve.
- Markdown: Simpler, easier to learn.
- Use Cases:
- LaTeX: Best for complex documents, scientific papers, and books.
- Markdown: Best for web content, simple documents, and note-taking.
- Mathematical equations:
- LaTex is the best for complex mathematical equations.
- Markdown can display mathematical equations, but it usualy does this by embedding LaTex code.
In essence, if you need to create a highly formatted document with complex mathematical equations, LaTeX is the better choice.
If you need to create simple, easy-to-read text documents or web content, Markdown is the more practical option.
- I was also exploring how to create a CV with AI, based on open source CV as a Code
Latex themes for CVs
There are some excellent LaTeX themes specifically designed for CV/resume building.
🎯 Popular CV/Resume LaTeX Themes
1. ModernCV (Most Popular)
- Professional and clean design
- Multiple color schemes (blue, orange, green, red, grey, black)
- Multiple styles (casual, classic, banking, fancy)
- Easy to customize
2. AwesomeCV
- Modern, minimalist design
- Great for tech professionals
- Clean typography and spacing
3. Friggeri CV
- Elegant sidebar layout
- Professional appearance
- Good for academic/research positions
4. AltaCV
- Modern design with sidebar
- Great for developers and designers
- Supports multiple layouts
🚀 Let’s Install and Try ModernCV
Great! ModernCV is already available. Let me create a sample CV template for you:
Now let's compile this CV to see how it looks:
Great! The CV compiled successfully! The error about the missing `picture` file is just because we referenced a photo that doesn't exist. Let's check the generated PDF:
Perfect! Now let me show you how to use Pandoc with CV templates. Let me create a markdown version of a CV that can be converted using Pandoc:
Now let's convert this markdown CV to PDF using our Eisvogel template:
Great! It worked (just some emoji warnings which is normal). Let's also create a version without emojis for better compatibility:🎯 CV/Resume LaTeX Themes - Complete Guide
Perfect! You now have multiple CV options. Here’s what we’ve created:
✅ What We Built:
sample-cv.pdf(29 KB) - Pure LaTeX ModernCV templatecv-eisvogel.pdf(33 KB) - Markdown → Eisvogel templatecv-clean.pdf(33 KB) - Clean markdown → Eisvogel (no emojis)
🎨 Available CV Themes:
1. ModernCV (Pure LaTeX)
# Direct LaTeX compilation
xelatex sample-cv.tex- Styles:
classic,casual,banking,fancy - Colors:
blue,orange,green,red,grey,black - Features: Professional layout, automatic formatting
2. Pandoc + Eisvogel (Markdown → PDF)
# Markdown to professional PDF
pandoc cv-template.md -o cv.pdf --template=eisvogel-working.latex --pdf-engine=xelatex- Benefits: Write in markdown, get professional PDF
- Flexibility: Easy to edit and version control
3. Other Popular CV Themes:
- AwesomeCV - Modern, minimalist
- Friggeri CV - Elegant sidebar layout
- AltaCV - Modern with sidebar
- Twenty Second Resume - Clean, simple
💡 CV Building Workflow:
Choose your approach:
- Pure LaTeX for maximum control
- Markdown + Pandoc for simplicity
Pick your template:
- ModernCV for traditional resumes
- Eisvogel for modern, clean look
- Custom templates for unique designs
Generate multiple formats:
# PDF for applications pandoc cv.md -o cv.pdf --template=eisvogel-working.latex # HTML for web pandoc cv.md -o cv.html --css=cv-style.css # Word for HR systems pandoc cv.md -o cv.docx
🚀 Pro Tips:
- Version control your markdown CV
- A/B test different templates for different applications
- Keep it simple - focus on content, not fancy formatting
- Use consistent formatting - same date format, bullet style, etc.
You now have a complete CV building system! Would you like me to show you how to customize any of these templates further, or create additional CV variations?
Historieta
HR might as you with these, so be prepared:
- A situation where you lead digital transformation and modified/shaped a product
- What are you looking for in your career?
I am seeking a role that blends technology, data, and business acumen, allowing me to orchestrate data-driven solutions that resonate with client’s need at the highest professional level.
Im guessing that you are focusing into a D&A related role, consider adapting these into any field, like telecom or FCMG/SCM
Questions to HR
- How does the on boarding looks like - To the company and project?
- Are there any colleagues already on boarded? in which roles?
- How does the tech interview looks like?
- How do you define success in the team?
- what does it mean success in this position? how do you measure it?
- what do u like the most working for this company?
- what key features a person need to be a good cultural fit for the company?
- what are the current company goals and how this team/role is supporting them?
- Regarding priority management What is the work methodology that is implemented in the team? Kanban? Scrum?
- What are other departments that we collaborate with? How does the marketing team work with other teams in the company.
- What is the business domain of the customers that we are expected to work for?
- What opportunities for professional development and learning are available?
In addition to my professional experience, I actively maintain a tech blog where I share insights, methodologies, and best practices in analytics.
This platform not only demonstrates my deep commitment to the field but also shows my enthusiasm for collaborating and sharing knowledge with the broader community.
QQs to managers
What kinds of data will I have access to?
What tools and technologies does the team currently use for data science work?
What is the biggest challenge your team is currently facing in making the most out of your data?
Can you describe the company’s vision for the future of data analytics and how this role fits into that vision?
What is the team’s approach to handling unexpected challenges or roadblocks in data analytics projects?
trusted advisor of products - 1 person dedicated to 1 squad
Can you describe any ongoing or upcoming business development projects that involve data analytics, and how this role would be involved?
How does the company foster collaboration between the data analytics and business development teams to ensure data-driven strategies are effectively implemented?
How do you promote knowledge sharing and collaboration among team members to ensure continuous improvement in data practices?
For BAs/PMs
These are excellent and comprehensive questions for a BA/PM interview preparation.
They cover core competencies essential for success in both roles.
Here’s a breakdown of why each question is effective and what to focus on when answering them.
Accountability: Leading and Taking Responsibility for Projects
This question assesses your sense of ownership and leadership. A good answer will show you don’t just complete tasks, but you also take ultimate responsibility for the project’s success or failure.
- What to Prepare: Think of a specific project where you took charge. Describe a situation where you had to make a tough decision or where something went wrong.
Focus on what you did to rectify the situation and how you learned from it. Avoid blaming others.
The interviewer wants to see that you’re proactive and resilient.
- Key Skills to Highlight: Leadership, ownership, problem-solving, resilience, and proactivity.
Resolving Difficult Conflicts
This question tests your interpersonal skills and emotional intelligence. In any project, conflicts are inevitable, and how you handle them is crucial.
- What to Prepare: Have a story ready about a conflict you faced, perhaps between a stakeholder and a developer, or within the development team itself. Walk through the steps you took to understand both sides of the issue.
A good approach is to describe how you facilitated a discussion, found common ground, and arrived at a solution that satisfied everyone (or at least was a mutually acceptable compromise).
- Key Skills to Highlight: Mediation, negotiation, communication, empathy, and active listening.
Analyzing Business Needs and Taking Requirements Easy for Development Team
This is the core of the Business Analyst (BA) role and a key part of the Project Manager (PM) role. This question evaluates your ability to translate high-level business goals into actionable, clear requirements.
- What to Prepare: Describe your process for gathering and documenting requirements. Explain how you use techniques like user stories, use cases, or process flows. Emphasize how you ensure the requirements are clear, concise, and non-ambiguous for the technical team. You might mention how you clarify assumptions and get buy-in from all parties.
- Key Skills to Highlight: Requirement elicitation, documentation, communication, analytical thinking, and a solid understanding of agile/scrum methodologies.
Cooperation with Development Team and Planning
This question focuses on your collaborative and organizational skills. A strong relationship with the development team is critical for project success.
What to Prepare: Talk about how you work with the development team, not just at them. Describe how you involve them in the planning process, perhaps through sprint planning meetings or backlog grooming sessions. Highlight how you ensure they have the resources and information they need to succeed. Explain how you handle changes to the plan and communicate them effectively.
Key Skills to Highlight: Collaboration, communication, planning, organizational skills, and adaptability.