Reasons why I love Containers. With Cloudflared and AI Apps.
Intro
A Container and related tools recap post.
Using Containers to pack all Python dependencies
Container Tech is Cool
Containers are an essential tool for simplifying creating and self-hosting software.
They give us:
- Portability: Containers ensure that your software runs consistently across different environments (development, testing, production).
- Scalability: Easily replicated and orchestrated, containers allow for dynamic scaling, particularly in cloud environments.
- Isolation: Containers isolate applications, preventing conflicts between dependencies.
- Efficiency: Containers share the host OS kernel, making them more resource-efficient and faster than virtual machines.
More?
Coderized have a couple of very interesting and well edited videos about containers.
Why Docker got easier? 📌
Simplifying Containerization with Docker
Docker Init: Simplifies containerizing new and existing projects by offering pre-configured development templates. This automates setup, enabling faster building and deployment.
Docker Debug: Streamlines container debugging by injecting necessary packages at runtime without filesystem modifications. Includes a built-in toolbox, access to the Nix package repository, remote debugging, metadata analysis, and log auditing.
Docker Compose Watch: Improves the development workflow by synchronizing local files with containers and enabling actions like filtering, restarting, and rebuilding containers based on file changes.
Docker Build Cloud: Offloads container building to a cloud service, significantly reducing build times (up to 39x) and saving developers an average of one hour per day.
Docker Scout: Enhances container security by identifying and addressing vulnerabilities, policy violations, and outdated dependencies, often automatically.
Takeaways
- Ease of Use: Docker init simplifies project containerization.
- Efficient Debugging: Docker debug provides versatile and efficient debugging tools.
- Streamlined Development: Docker compose watch improves the development loop with live file synchronization.
- Increased Productivity: Docker Build Cloud accelerates build times and saves developer time.
- Enhanced Security: Docker Scout proactively addresses security issues in containers.
What Are Containers?
Containers are lightweight, portable, and self-contained units of software that package an application along with its dependencies, libraries, and configurations.
This makes it possible to run the software seamlessly across different environments.
Unlike virtual machines, containers share the host system’s OS kernel, making them faster to deploy and more efficient.
Prerequisites for Containers
Before you can use containers, you need to set up the required tools. Below are the steps for setting up Docker and Podman, two of the most popular containerization tools.
Docker Setup
- Install Docker:
- On Linux:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install docker.io
sudo systemctl start docker
sudo systemctl enable docker- For more installation details, check Docker’s official guide.
- Verify Installation:
- Check Docker version:
docker --version- Run a simple container to test:
docker run hello-world- Post-Installation:
- To avoid using
sudowith Docker commands on Linux:
- To avoid using
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER- Start Using Docker:
- Common commands:
docker build,docker run,docker ps. Try pulling images from Docker Hub (e.g.,docker pull ubuntu).
- Common commands:
Podman Setup
- Install Podman:
- On Linux:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install podman- Verify Installation:
- Check the Podman version:
podman --version- Test Podman:
- Run a test container:
podman run hello-world- Post-Installation:
- Add your user to the Podman group:
sudo usermod -aG podman $USER- Start Using Podman:
- Podman commands are similar to Docker’s. Start using commands like
podman build,podman run, andpodman ps.
- Podman commands are similar to Docker’s. Start using commands like
UI Tools for Managing Containers 📌
While Docker and Podman are command-line tools, there are several UI tools that make managing containers easier and more intuitive. Here are some popular options:
- Portainer
- Platform: Linux, Windows, macOS
- Portainer is a popular open-source web-based UI for managing Docker and Podman containers.
- Installation Command:
sudo docker run -d -p 8000:8000 -p 9000:9000 --name=portainer --restart=always -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock -v portainer_data:/data portainer/portainer-ceAccess Portainer at: http://localhost:9000.
- Dockge
- Platform: Docker-based UI for container management.
- Installation Command:
docker run louislam/dockge:1 -d \
--name dockge \
--restart unless-stopped \
-p 5001:5001 \
-v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock \
-v /home/jalcocert/Documents/Dockge/data:/app/data \
# -v /home/your_user/Desktop/Dockge/data:/app/data \Access Dockge at: http://localhost:5001.
- Cockpit
- Platform: Linux (CentOS, Fedora, Ubuntu)
- Cockpit is a server management tool with a web-based UI for container management.
- Installation Command:
sudo apt install cockpit
sudo systemctl enable --now cockpit.socket- Kitematic (for Docker)
- Platform: Windows/macOS
- Kitematic is a simple GUI for Docker that makes it easier to create, configure, and run containers.
- Yacht
- Platform: Web-based UI for Docker containers.
- Learn more about Yacht from this video or check its GitHub page.
These tools simplify the process of managing containers, especially if you prefer not to work exclusively with the command line.
Setting up Docker or Podman is straightforward, and with UI tools like Portainer, Dockge, and others, managing your containers has never been easier.
Easy SelfHosting with Containers
Why Docker is great to deploy to a VPS? 📌
Dreams of Code, a Senior NYT Reporter, explains their preference for Docker Stack over Docker Compose for VPS deployments.
- Secrets Management: Docker Stack allows external secrets management, separate from the Docker Stack YAML file, which can be linked to environment variables for database and web app services. This promotes secure secret storage.
- Redeploying Applications: Docker Compose can lead to downtime during redeployments as it shuts down running services before deploying upgrades. Manually copying the Docker Compose YAML file also hinders agile deployments.
- Docker Stack Deployment: Docker Stack extends Docker Compose by deploying Docker Compose files on a Docker Swarm enabled node. Swarm mode provides features like blue-green deployments, rolling releases, secure secrets management, service rollbacks, and clustering.
- Automated Deployments: Docker Stack integrates with GitHub Actions for automated deployments. GitHub Actions pipeline workflow files manage the Docker Stack deployment process.
Key Takeaways: * Docker Stack improves upon Docker Compose for seamless and secure VPS application deployments. * Docker Context simplifies managing and deploying to multiple VPS instances from a workstation. * Docker Stack’s secrets management, rollback capabilities, and built-in load balancing enhance production services and developer experience. * Combining Docker Stack with GitHub Actions streamlines CI/CD, ensuring fast, secure deployments with minimal manual effort.
Exposing Apps Safely with Cloudflare Tunnels
Learn how to securely expose your self-hosted services (Including AI Apps!) using Cloudflare’s Zero Trust Tunnel with Docker
What is Cloudflare Zero Trust Tunnel?
Cloudflare Zero Tunnel creates a secure connection between your local machine and Cloudflare’s global edge network.
It allows private resources to be accessed without exposing them to the public internet, providing enhanced security and privacy.
Key Benefits:
- Improved Security: End-to-end encryption (TLS 1.3) for safe data transmission.
- Increased Privacy: Avoid exposing private resources to the public internet.
- Global Accessibility: Access your services securely from anywhere.
- Faster Connections: QUIC protocol for more reliable and faster connections.
Docker allows you to containerize and deploy applications easily.
By combining Docker with Cloudflare Zero Tunnel, we can securely expose services on the internet.
Create a Docker container for your service
Use Docker to package your application, such as a Python-based web service, in a container.Install Cloudflare Zero Tunnel Client
- Use the Cloudflare cloudflared Docker image.
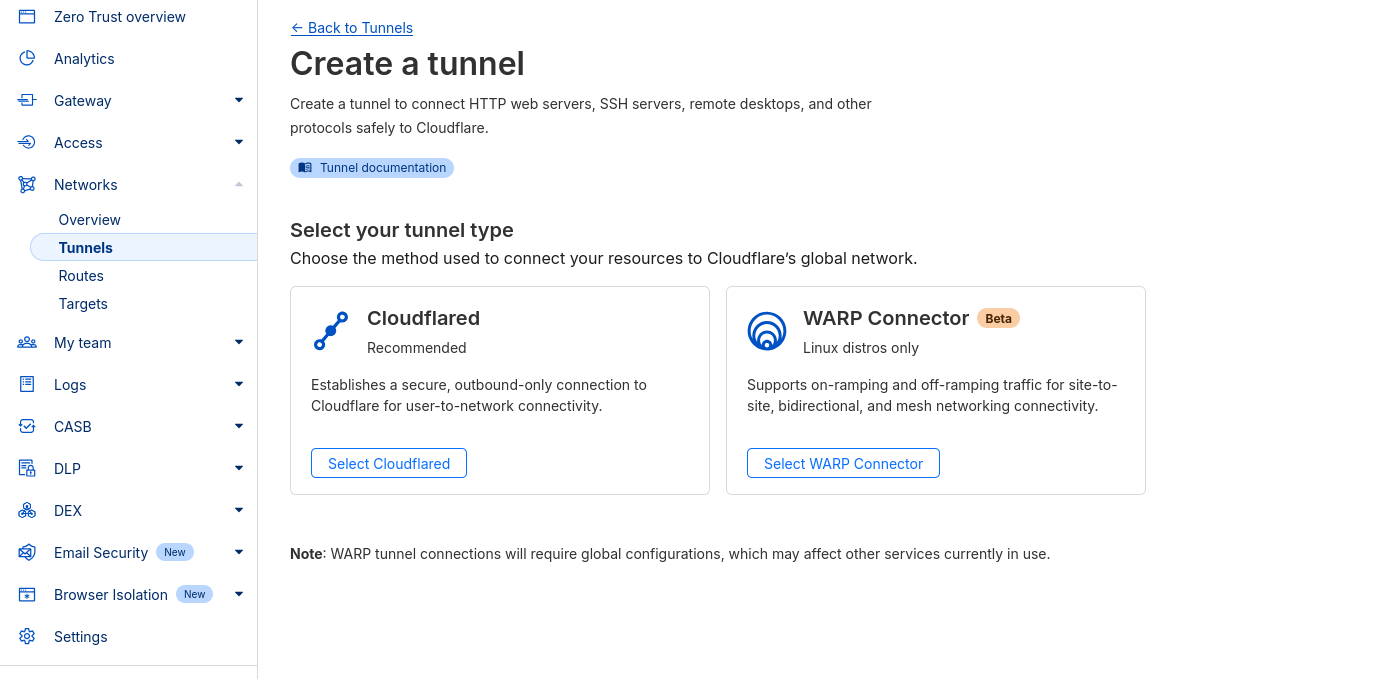
- Configure the Cloudflare Zero Tunnel by setting up a token in the Cloudflare Dashboard.
Set Up Cloudflare Tunnel with Docker
- Run
cloudflaredas a container linked to your own services:
- Run
#it will be created automatically and called: cloudflared_tunnel as per the <containername><networkname>
#docker network create tunnel#version: '3.8'
services:
cloudflared:
image: cloudflare/cloudflared:latest
container_name: cloudflared
command: tunnel --no-autoupdate run --token token_from_cloudflare_webUI #see video below
networks:
- tunnel #a name for the Cloudflare Network
restart: always #unless-stopped
networks:
tunnel: #a name for the Cloudflare Network- Connect Your Service to the Tunnel Network
Add your service container to the Cloudflare tunnel network:
docker network connect tunnel your_service_container- Configure a Public Hostname on Cloudflare
In the Cloudflare Dashboard, create a public hostname for your service, linking it to the service container using the formatyour_service_name:docker_port.
Is my home IP safe with Cloudflare? 📌
How to check my local IP address?
ifconfigHow to check the exposed service IP?
Cloudflare Tunnel ensures your service is securely exposed without revealing your local IP:
curl your_selected_domain.comBy following this guide, you can expose your services securely without the need for port forwarding or exposing your home IP.
Cloudflare’s Zero Trust Tunnel with Docker is a powerful solution to enhance both security and accessibility of your self-hosted applications.
Plus, you get https out of the box!
Creating Containers
Just recently, we can use not only x86 VM with github to build our containers, but also native ARM (we can skip emulating it with QEMU).
if you want to create containers on your own hardware (but automatically), you can use:
- Github/Gitlab Runners
- Gitea Act Runner
- Jenkins CI/CD
- Argo CI/CD
Is my home IP safe with Cloudflare? 📌
Argo CD is a declarative, GitOps continuous delivery tool specifically designed for Kubernetes.
It operates based on the principle that your Git repository serves as the single source of truth for your desired application state.
How Argo CD works?
- Define Desired State: You define your desired application state (e.g., deployments, services, configurations) in your Git repository using Kubernetes manifests.
- Argo CD Monitors: Argo CD continuously monitors your Git repository for changes.
- Automatic Synchronization: When changes are detected, Argo CD automatically synchronizes your Kubernetes cluster to match the desired state defined in Git.
- Continuous Reconciliation: Argo CD constantly compares the actual state of your cluster with the desired state in Git. If discrepancies are found, it takes corrective actions to bring the cluster back in sync.
Comparison with Jenkins and GitHub Actions:
| Feature | Argo CD | Jenkins | GitHub Actions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Focus | Kubernetes-native GitOps CD | General-purpose CI/CD | CI/CD specifically for GitHub |
| Deployment Model | Pull-based (Git as source of truth) | Push-based (CI/CD system triggers deployments) | Push-based |
| Strengths | Excellent for Kubernetes deployments, strong GitOps implementation, declarative approach | Highly flexible and customizable, vast plugin ecosystem | Tight integration with GitHub, user-friendly interface |
| Weaknesses | Primarily focused on Kubernetes, might have a steeper learning curve for non-Kubernetes users | Can become complex for intricate pipelines, potential for configuration drift | Limited to GitHub repositories |
In essence:
Argo CD excels in Kubernetes environments, emphasizing GitOps principles for streamlined and reliable deployments.The bestThe best choice depends on your specific requirements, team expertise, and the complexity of your CI/CD pipelines. choice depends on your specific requirements, team expertise, and the complexity of your CI/CD pipelines.
Jenkins is a versatile platform suitable for various CI/CD needs, offering extensive customization options.
GitHub Actions provides a user-friendly, integrated solution for CI/CD workflows within the GitHub ecosystem.