Superset - Temperature Monitoring with Sensor (DS18B20) & TimeScaleDB
How to use Superset to visualize Temperature Data from DS18B20 Sensors
- The goal of this IoT Project - Get DS18B20 Temperature Data to Timescale & Superset
- The Python Script - Pushing DS18B20 Sensor Data from Python to TimeScaleDB
- Setup TimeScaleDB
- Configure Apache Superset for Visualization
The Sensor: DS18B20
The DS18B20 can detect: -55C to 125 Celsius
- Connection:
- Black cable - gnd
- Red - 3.3 to 5v
- Yellow - data –> to pin 7
- It needs a resistor. A 4.7K Ohm Resistor (Colour Code: Yellow Purple Red Gold)
- or 4.7k/10k resistor between data and 3.3v
The RPi4 with the DS18B20 sensor will look like:
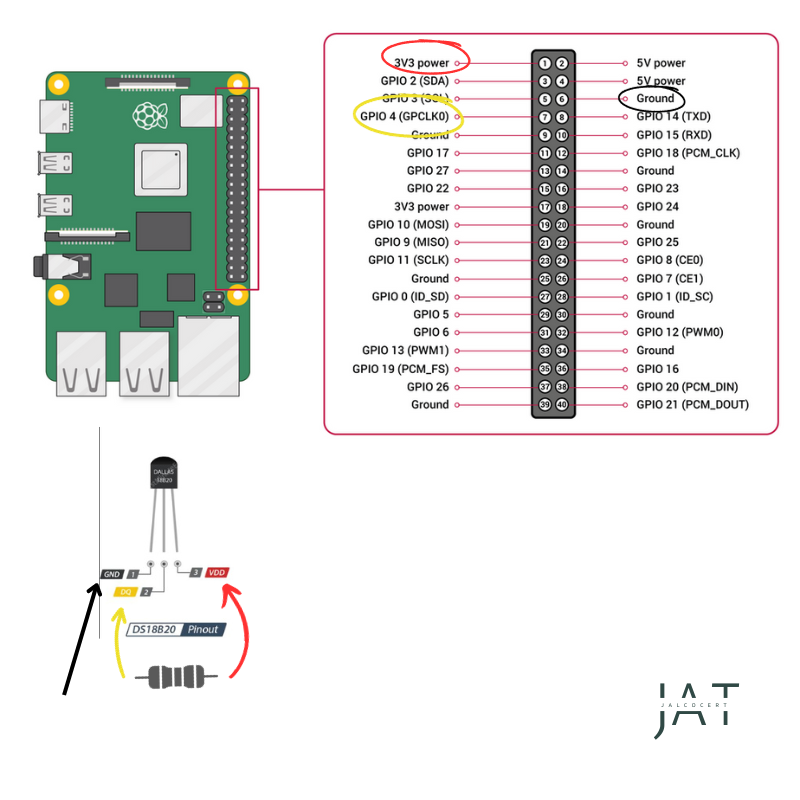 DS18B20 temperature sensor connection to a Raspberry Pi 4
DS18B20 temperature sensor connection to a Raspberry Pi 4
These videos were of great help to me:
1-wire must be enabled so that the RPi can read this sensor’s data.
connect the wiring and go to /sys/bus/w1/devices and find the folder with the serial number, then select the w1_slave file
The file should contain a YES in the first line.
Also, the video from ReefSpy helped me a lot with the initial setup plus the general idea of the Python code that can be used.
The Base Code: Python
Find the related project code here
Reading DS18B20 with Python
Create this Python script on your RPi.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
import os
import glob
import time
os.system('modprobe w1-gpio')
os.system('modprobe w1-therm')
base_dir = '/sys/bus/w1/devices/'
device_folder = glob.glob(base_dir + '28*')[0]
device_file = device_folder + '/w1_slave'
def read_temp_raw():
f = open(device_file, 'r')
lines = f.readlines()
f.close()
return lines
def read_temp(scale):
lines = read_temp_raw()
while lines[0].strip()[-3:] != 'YES':
time.sleep(0.2)
lines = read_temp_raw()
equals_pos = lines[1].find('t=')
if equals_pos != -1:
temp_string = lines[1][equals_pos+2:]
temp_c = float(temp_string) / 1000.0
temp_f = temp_c * 9.0 / 5.0 + 32.0
if scale == "F":
return "{:.1f}".format(temp_f)
if scale =="C":
return "{:.1f}".format(temp_c)
else:
return temp_c, temp_f
while True:
print(read_temp("C"))
time.sleep(1)
Execute it with:
1
python3 dsb.py
Pushing Data from Python to Timescale
We have 3 mandatory components for this to work:
- The adjusted Python code that pushed data: https://github.com/JAlcocerT/RPi/Z_IoT/DS18B20-to-TimeScaleDB/Python2TimeScale.py
- https://github.com/JAlcocerT/RPi/Z_IoT/DS18B20-to-TimeScaleDB/Python2TimeScale-Stack.yml
- The docker image that isolates all of this and allow us to deploy easier: https://hub.docker.com/r/fossengineer/iot/tags
- The tag is: ds18b20_sensor_to_timescale
And another one if you want to replicate the docker build process:
- The https://github.com/JAlcocerT/RPi/Z_IoT/DS18B20-to-TimeScaleDB/Dockerfile>
FAQ
How can I query TimeScaleDB?
You will have to login to the container:
1
docker run -it --rm --network=dsbtimescale_dsb_network postgres psql -h timescaledb_dsb_container -U myuser -d mydb --username=myuser
Then execute:
1
psql -U myuser -d mydb
And then qrite your SQL Queries:
1
2
3
SELECT * FROM ds18b20_sensor;
SELECT MAX(temperature) FROM ds18b20_sensor;
SELECT * FROM ds18b20_sensor ORDER BY time DESC LIMIT 1;
How to Setup Superset
Use this docker compose to setup Superset.
Thanks to:
- https://www.timescale.com/blog/data-visualization-in-postgresql-with-apache-superset/
- https://www.attilatoth.dev/speaking/timescaledb-superset/